| Trolleybuses in Dębica | |
|---|---|
 Church in Straszęcin, where once operated a trolleybus loop | |
 Route plates | |
| Overview | |
| Owner | Igloopol |
| Locale | |
| Transit type | trolleybus |
| Number of lines | 2 |
| Line number | 1-2 |
| Number of stations | 13 |
| Operation | |
| Began operation | 12 November 1988 |
| Ended operation | October 1990 |
| Operator(s) | Igloopol |
| Number of vehicles | 10 |
The Dębica trolleybus system was a trolleybus network operated by agro-industrial works Igloopol[1] in Dębica and Straszęcin, Poland between 12 November 1988 and October 1990.[2]
By the standards of the various now-defunct trolleybus systems in Poland, the Dębica system was a very small one, with only two routes, and a maximum fleet of just 10 trolleybuses.
History
The first construction stage assumed the construction of an overhead line, which was to connect the Dębica railway station with Igloopol plants in Dębica and Straszęcin. The second construction stage involved the expansion of the network in the city center and to Zawada and Latoszyn.[3] On 25 August 1988, the Municipal National Council in Dębica did not agree to the expansion of the network in Dębica (this decision was criticized both by residents and the creator of Dębica trolleybuses, Edward Brzostowski[4]). Currently, the overhead lines do not exist - they have been dismantled. Numerous overhead line poles remained as streetlamps.[1]
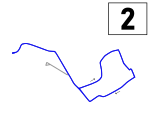
Lines
Detailed system scheme
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
References
Notes
- ^ a b Powałka, Anna (2010). "Zlikwidowane sieci trolejbusowe w Polsce" (PDF). Acta Geographica Silesiana – via Wydział Nauk o Ziemi Uniwersytetu Śląskiego.
- ^ Rowiński, Tomasz (2017-11-08). "Bardzo krótka historia trolejbusów w Dębicy". Wiadomości Dębickie (in Polish). Retrieved 2020-06-13.
- ^ Redakcja (2015-10-09). "Trolejbusy wrócą do Dębicy?". Dębica Nasze Miasto (in Polish). Retrieved 2020-06-13.
- ^ "Edward Brzostowski patronem osiedla w Dębicy - gospodarkaPodkarpacka.pl". gospodarkapodkarpacka.pl. Retrieved 2020-06-13.
External links
![]() Media related to Trolleybuses in Dębica at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Trolleybuses in Dębica at Wikimedia Commons