Tripodal ligands are tri- and tetradentate ligands. They are popular in research in the areas of coordination chemistry and homogeneous catalysis. Because the ligands are polydentate, they do not readily dissociate from the metal centre. Many tripodal ligands have C3 symmetry.
Coordination chemistry
In their coordination complexes with an octahedral molecular geometry the tridentate tripod ligands occupy one face, leading to a fixed facial (or fac) geometry. The tetradentate tripodal ligands occupy four contiguous sites, leaving two cis positions available on the octahedral metal center. When bound to four- and five-coordinate metal centres, these ligands impose C3 symmetry, which can lead to uncommon ligand field splitting patterns. Tripodal ligands are often able to coordinately saturate metal ions with lower coordination numbers.
One tripodal ligand of commercial significance is nitrilotriacetate, N(CH2CO2−)3 because it is cheaply produced and has a high affinity for divalent metal ions. Other tripodal triamine ligands include tren (N(CH2CH2NH2)3) and cis-1,3,5-triaminocyclohexane.[1] Certain triphosphines such as RC(CH2PPh2)3 are also tripodal. Many kinds of donor groups have been incorporated into the arms of tripodal ligands, including amido (R2N−),[2] and N-heterocyclic carbenes.

- Tripodal Ligands Examples
-
A tripodal triphosphines, X can be CR, SiR, Si−, BR−, B, N, P etc.[4]
-
-
Structure of a metal complex of trispyrazolylborate, an anionic tridentate tripod ligand.[6]
-
NTA is a commercially important tripodal ligand. Its three carboxylic acid groups undergo deprotonation upon complexation.
-
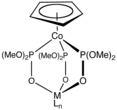
The Kläui ligand, a dianionic organometallic ligand.
-
-
-
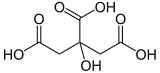
citric acid, when triply deprotonated, is an unsymmetrical tripodal ligand.
References
- ^ Aimee J. Gamble; Jason M. Lynam; Robert J. Thatcher; Paul H. Walton; Adrian C. Whitwood (2013). "cis-1,3,5-Triaminocyclohexane as a Facially Capping Ligand for Ruthenium(II)". Inorg. Chem. 52 (8): 4517–4527. doi:10.1021/ic302819j. PMID 23517123.
- ^ Verkade, J. G. (1993). "Atranes: New Examples with Unexpected Properties". Acc. Chem. Res. 26 (9): 483. doi:10.1021/ar00033a005.
- ^ Schwarzenbach, Gerold; Bürgi, Hans-Beat; Jensen, William P.; Lawrance, Geoffrey A.; Mønsted, Lene; Sargeson, Alan M. (1983). "Acid Cleavage of Nickel(Ii) Complexes Containing cis,cis-1,3,5-Cyclohexanetriamine (TACH), Crystal Structure of [Ni(tach)(H2O)3](NO3)2, and a Correlation Between the Structure and Reactivity of Nickel-Polyamine Complexes". Inorganic Chemistry. 22 (26): 4029–4038. doi:10.1021/ic00168a042.
- ^ Saouma, C. T., Peters, J. C. (2011). "M-E and M=E Complexes of Iron and Cobalt that Emphasize Three-Fold Symmetry (E = O, N, NR)". Coord. Chem. Rev. 255 (7–8): 920–937. doi:10.1016/j.ccr.2011.01.009. PMC 3103469. PMID 21625302.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Blackman, A. G. (2008). "Tripodal Tetraamine Ligands Containing Three Pyridine Units: the other polypyridyl ligands". Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2008 (17): 2633. doi:10.1002/ejic.200800115.
- ^ Parkin, G. (2000). "The Bioinorganic Chemistry of Zinc: Synthetic Analogues of Zinc Enzymes that Feature Tripodal Ligands". Chemical Communications (20): 1971–1985. doi:10.1039/B004816J.

![A tripodal triphosphines, X can be CR, SiR, Si−, BR−, B, N, P etc.[4]](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/e/ea/TripodalPhosphine.png/160px-TripodalPhosphine.png)
![Tris(2-pyridylmethyl)amine, a tetradentate tripodal ligand popular in bioinorganic chemistry.[5]](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/2/2b/Tris%28pyridylmethyl%29amine_%28structural_diagram%29.png/83px-Tris%28pyridylmethyl%29amine_%28structural_diagram%29.png)
![Structure of a metal complex of trispyrazolylborate, an anionic tridentate tripod ligand.[6]](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/8/86/LnMTp.png/135px-LnMTp.png)