| Solitary tract | |
|---|---|
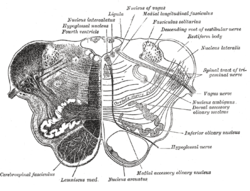 Transverse section of medulla oblongata below the middle of the olive. (Fasciculus solitarius labeled at upper right.) | |
 The formatio reticularis of the medulla oblongata, shown by a transverse section passing through the middle of the olive. (#15 is fasciculus solitarius) | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | tractus solitarius medullae oblongatae |
| NeuroNames | 785 |
| NeuroLex ID | birnlex_1483 |
| TA98 | A14.1.04.120 |
| TA2 | 6048 |
| FMA | 72618 |
| Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy | |
The solitary tract (tractus solitarius or fasciculus solitarius) is a compact fiber bundle that extends longitudinally through the posterolateral region of the medulla oblongata. The solitary tract is surrounded by the solitary nucleus, and descends to the upper cervical segments of the spinal cord. It was first named by Theodor Meynert in 1872.
YouTube Encyclopedic
-
1/3Views:5 8896 5661 111
-
Mean Arterial Pressure Control - Usmle CVS Physiology animated lecture
-
How Do We Taste?
-
Baroreflex
Transcription
Composition
The solitary tract is made up of primary sensory fibers and descending fibers of the vagus, glossopharyngeal, and facial nerves.
Function
The solitary tract conveys afferent information from stretch receptors and chemoreceptors in the walls of the cardiovascular, respiratory, and intestinal tracts. Afferent fibers from cranial nerves 7, 9 and 10 convey taste (SVA) in its rostral portion, and general visceral sense (general visceral afferent fibers, GVA) in its caudal part. Taste buds in the mucosa of the tongue can also generate impulses in the rostral regions of the solitary tract. The efferent fibers are distributed to the solitary tract nucleus.
Synonyms
There are numerous synonyms for the solitary tract:
- round fasciculus (Latin: fasciculus rotundus)
- solitary fasciculus (Latin: fasciculus solitarius)
- solitary bundle (Latin: funiculus solitarius)
- Gierke respiratory bundle (Named for German anatomist Hans Paul Bernhard Gierke).[1]
- Krause respiratory bundle (Named for German anatomist Johann Friedrich Wilhelm Krause).[1]
References
- Stedman, Thomas Lathrop (2006). Stedman's Medical Dictionary, 28th edition. Baltimore, MD: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. p. 2011. ISBN 0-7817-3390-1.
- ^ a b Stedman's Medical Eponyms by Thomas Lathrop Stedman; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2005 - Medical - 899 pages
