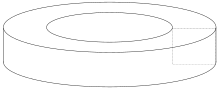

In mathematics, a toroid is a surface of revolution with a hole in the middle. The axis of revolution passes through the hole and so does not intersect the surface.[1] For example, when a rectangle is rotated around an axis parallel to one of its edges, then a hollow rectangle-section ring is produced. If the revolved figure is a circle, then the object is called a torus.
The term toroid is also used to describe a toroidal polyhedron. In this context a toroid need not be circular and may have any number of holes. A g-holed toroid can be seen as approximating the surface of a torus having a topological genus, g, of 1 or greater. The Euler characteristic χ of a g holed toroid is 2(1-g).[2]
The torus is an example of a toroid, which is the surface of a doughnut. Doughnuts are an example of a solid torus created by rotating a disk, and should not be confused with toroids.
Toroidal structures occur in both natural and synthetic materials.[3]
YouTube Encyclopedic
-
1/3Views:39 3361 327 521583 683
-
Magnetic Field of a Toroidal Solenoid, Ampere's Law, Physics & Electromagnetism
-
The Mathematics of our Universe
-
Embedding a Torus (John Nash) - Numberphile
Transcription
Equations
A toroid is specified by the radius of revolution R measured from the center of the section rotated. For symmetrical sections volume and surface of the body may be computed (with circumference C and area A of the section):
Square toroid
The volume (V) and surface area (S) of a toroid are given by the following equations, where A is the area of the square section of side, and R is the radius of revolution.
Circular toroid
The volume (V) and surface area (S) of a toroid are given by the following equations, where r is the radius of the circular section, and R is the radius of the overall shape.
See also
Notes
- ^ Weisstein, Eric W. "Toroid". MathWorld.
- ^ Stewart, B.; "Adventures Among the Toroids:A Study of Orientable Polyhedra with Regular Faces", 2nd Edition, Stewart (1980).
- ^ Carroll, Gregory T.; Jongejan, Mahthild G. M.; Pijper, Dirk; Feringa, Ben L. (2010). "Spontaneous generation and patterning of chiral polymeric surface toroids". Chemical Science. 1 (4): 469. doi:10.1039/c0sc00159g. ISSN 2041-6520.
External links
 The dictionary definition of toroid at Wiktionary
The dictionary definition of toroid at Wiktionary




