| 58th Boat Race | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Date | 30 March 1901 | ||
| Winner | Oxford | ||
| Margin of victory | 2/5 of a length | ||
| Winning time | 22 minutes 31 seconds | ||
| Overall record (Cambridge–Oxford) | 24–33 | ||
| Umpire | Frank Willan (Oxford) | ||
| |||
The 58th Boat Race took place on 30 March 1901. Held annually, the Boat Race is a side-by-side rowing race between crews from the Universities of Oxford and Cambridge along the River Thames. Cambridge had won the previous year's race by twenty lengths. This year's race, umpired by former rower Frank Willan, was won by Oxford by two-fifths of a length in a time of 22 minutes 31 seconds. Oxford's crew featured five former Blues while Cambridge just one. It was the Dark Blues' first win three years and the slowest winning time since 1877. The victory took the overall record in the event to 33–24 in favour of Oxford.
YouTube Encyclopedic
-
1/3Views:1 42311 493160 917
-
The America's Cup Yacht Race
-
UW Men's Championship Crew 2015
-
Who Really Invented the Radio?
Transcription
Background

The Boat Race is a side-by-side rowing competition between the University of Oxford (sometimes referred to as the "Dark Blues")[1] and the University of Cambridge (sometimes referred to as the "Light Blues").[1] The race was first held in 1829, and since 1845 has taken place on the 4.2-mile (6.8 km) Championship Course on the River Thames in southwest London.[2][3] The rivalry is a major point of honour between the two universities; it is followed throughout the United Kingdom and as of 2014, broadcast worldwide.[4] Cambridge went into the race as reigning champions, having won the 1900 race by twenty lengths, while Oxford led overall with 32 victories to Cambridge's 24 (excluding the "dead heat" of 1877).[5][6]
Oxford's coaches were G. C. Bourne who had rowed for Oxford in the 1882 and 1883 races, Harcourt Gilbey Gold (Dark Blue president the previous year and four-time Blue) and C. K. Philips who had represented Oxford four times between 1895 and 1898.[7] Cambridge were coached by James Brookes Close, who had rowed for the Light Blues three times between 1872 and 1874, Stanley Muttlebury, five-time Blue between 1886 and 1890 and John Ernest Payne (two-time Blue in 1899 and 1900).[7] The umpire for the race for the twelfth year in a row was Frank Willan who won the event four consecutive times, rowing for Oxford in the 1866, 1867, 1868 and 1869 races.[8]
Author and former Oxford rower George Drinkwater wrote that the Dark Blues "created a sensation" when they elected to row in a boat designed by Felix Warre, based on that built by Matthew Taylor of Newcastle upon Tyne for the 1857 race.[9] Of the crew, Drinkwater remarked "the material of which [they were] built was second class, but behind Culme-Seymour a, and coached by Mr. Gold ... they attained very nearly to first-class pace".[9] The Cambridge crew suffered illness in practice and in a late reorganisation, "the crew received a set-back from which they never really recovered."[9]
Crews
The Oxford crew weighed an average of 12 st 2.675 lb (77.2 kg), 1.375 pounds (0.62 kg) per rower more than their opponents.[10] The Cambridge crew contained a single rower with Boat Race experience in their number three, boat club president Bertram Willes Dayrell Brooke. Conversely, Oxford saw five former Blues return to the boat, including rower Warre and cox Gilchrist Maclagan who were making their third appearance in the event.[10] All of the participants in the race were registered as British.[11] Seven of the nine Cambridge crew members were studying at Trinity College.[10]
| Seat | Oxford |
Cambridge | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Name | College | Weight | Name | College | Weight | |
| Bow | F. O. J. Huntley | University | 11 st 7 lb | R. H. Nelson | 3rd Trinity | 11 st 3 lb |
| 2 | H. C. de J. Du Vallon | Brasenose | 12 st 4.5 lb | B. C. Cox | Trinity Hall | 12 st 0 lb |
| 3 | J. Younger | New College | 12 st 11.5 lb | B. W. D. Brooke (P) | 1st Trinity | 11 st 9.5 lb |
| 4 | A. de L. Long | New College | 12 st 9.5 lb | C. W. H. Taylor | 3rd Trinity | 12 st 7.5 lb |
| 5 | H. J. Hale | Balliol | 12 st 10 lb | G. Parker | 1st Trinity | 12 st 5.5 lb |
| 6 | F. W. Warre (P) | Balliol | 12 st 7.5 lb | H. B. Grylls | 1st Trinity | 12 st 7 lb |
| 7 | T. B. Etherington-Smith | Oriel | 11 st 4.5 lb | E. F. Duncanson | Emmanuel | 12 st 5 lb |
| Stroke | R. H. Culme-Seymour | New College | 11 st 8.5 lb | G. M. Maitland | 1st Trinity | 12 st 1 lb |
| Cox | G. S. Maclagan | Magdalen | 8 st 3 lb | E. A. O. A. Jamieson | 1st Trinity | 8 st 6 lb |
| Source:[12] (P) – boat club president[13] | ||||||
Race
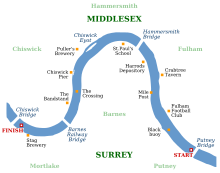
Cambridge won the toss and elected to start from the Surrey station, handing the Middlesex side of the river to Oxford.[10] Heavy rainstorms and strong wind from the south-west made for inclement conditions for the race. Willan started the race at 10:31 a.m. and Oxford, taking advantage of the bend in the river, gradually drew away from their opponents to hold a half-length lead by the Mile Post. The Cambridge stroke Graham Macdowall Maitland spurted to ensure that the crews were level by the time they passed Harrods Furniture Depository. Oxford's stroke rate dropped as they conceded ground to the Light Blues around the long side of the bend and dropped in behind them. Despite being closer to the shore, the water was still very rough and Cambridge struggled.[9]
However, Oxford found it impossible to move out into the rougher water to pass Cambridge and settled behind the Light Blues until near to Barnes Bridge where Maclagan moved and Culme-Seymour simultaneously spurted. As a result, they began to overlap the Cambridge, and with the bend of the river in their favour, they levelled the race as the crews passed Mortlake Brewery. Encountering more rough water, Cambridge were unable to respond and Oxford passed the finishing post two-fifths of a length ahead, in a time of 22 minutes 31 seconds.[14] It was the Dark Blues' first win in three years, and the slowest winning time since the 1877 race. The victory took the overall record in the event to 33–24 in favour of Oxford.[6]
References
Notes
- ^ a b "Dark Blues aim to punch above their weight". The Observer. 6 April 2003. Retrieved 20 August 2014.
- ^ Smith, Oliver (25 March 2014). "University Boat Race 2014: spectators' guide". The Daily Telegraph. Retrieved 20 June 2014.
- ^ "The Course". The Boat Race Company Limited. Retrieved 24 July 2014.
- ^ "Former Winnipegger in winning Oxford–Cambridge Boat Race crew". CBC News. 6 April 2014. Retrieved 20 August 2014.
- ^ "Classic moments – the 1877 dead heat". The Boat Race Company Limited. Archived from the original on 28 October 2014. Retrieved 11 November 2014.
- ^ a b "Men – Results". The Boat Race Company Limited. Retrieved 27 September 2014.
- ^ a b Burnell, pp. 110–111
- ^ Burnell, pp. 49, 59
- ^ a b c d Drinkwater, p. 109
- ^ a b c d Burnell, p. 67
- ^ Burnell, p. 39
- ^ Dodd, p. 314
- ^ Burnell, pp. 50–51
- ^ Drinkwater, p. 110
Bibliography
- Burnell, Richard (1979). One Hundred and Fifty Years of the Oxford and Cambridge Boat Race. Precision Press. ISBN 0950063878.
- Dodd, Christopher (1983). The Oxford & Cambridge Boat Race. Stanley Paul. ISBN 0091513405.
- Drinkwater, G. C.; Sanders, T. R. B. (1929). The University Boat Race – Official Centenary History. Cassell & Company, Ltd.


