Sulfinic acids are oxoacids of sulfur with the structure RSO(OH). In these organosulfur compounds, sulfur is pyramidal.[1]
YouTube Encyclopedic
-
1/3Views:5 8743 69010 634
-
Chem 201. Organic Reaction Mechanisms I. Lecture 19. Sulfur Chemistry
-
Cysteine
-
How Food Can Prevent Disease with Dr. Joel Fuhrman Spring Garden Tour
Transcription
Structure and properties
Sulfinic acids RSO2H are about 1000x more acidic than the corresponding carboxylic acid RCO2H. Sulfur is pyramidal, consequently sulfinic acids are chiral.
Preparation
They are often prepared in situ by acidification of the corresponding sulfinate salts, which are typically more robust than the acid. These salts are generated by reduction of sulfonyl chlorides.[2] An alternative route is the reaction of Grignard reagents with sulfur dioxide. Transition metal sulfinates are also generated by insertion of sulfur dioxide into metal alkyls, a reaction that may proceed via a metal sulfur dioxide complex. Unsubstituted sulfinic acid, when R is the hydrogen atom, is a higher energy isomer of sulfoxylic acid, both of which are unstable.
Examples
-
thiourea dioxide, a reducing agent used in textiles
-
hypotaurine, a biosynthetic intermediate
-
Rongalite, a source of "SO22−"
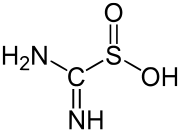
An example of a simple, well-studied sulfinic acid is phenylsulfinic acid. A commercially important sulfinic acid is thiourea dioxide, which is prepared by the oxidation of thiourea with hydrogen peroxide.[3]
- (NH2)2CS + 2H2O2 → (NH)(NH2)CSO2H + 2H2O
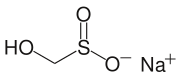
Another commercially important sulfinic acid is hydroxymethyl sulfinic acid, which is usually employed as its sodium salt (HOCH2SO2Na). Called Rongalite, this anion is also commercially useful as a reducing agent.
Sulfinates
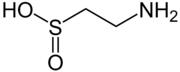
The conjugate base of a sulfinic acid is a sulfinate anion. The enzyme cysteine dioxygenase converts cysteine into the corresponding sulfinate. One product of this catabolic reaction is the sulfinic acid hypotaurine. Sulfinite also describes esters of sulfinic acid. Cyclic sulfinite esters are called sultines.
References
- ^ Saul Patai, ed. (1981). Sulphinic Acids, Esters and Derivatives. PATAI'S Chemistry of Functional Groups. John Wiley & Sons. doi:10.1002/9780470772270. ISBN 9780470772270.
- ^ Whitmore, F. C.; Hamilton, F. H. (1922). "Sodium p-Toluenesulfinic Acid". 2: 89. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.002.0089.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ^ D. Schubart "Sulfinic Acids and Derivatives" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry 2012, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. doi:10.1002/14356007.a25_461
External links
- Sulfinic+Acids at the U.S. National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
- Diagram at ucalgary.ca
- Diagram at acdlabs.com