| Submandibular triangle | |
|---|---|
 Submandibular triangle | |
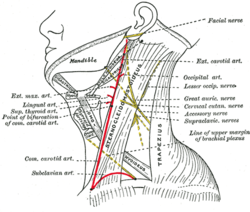 Side of neck, showing chief surface markings. (Nerves are yellow, arteries are red.) | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | trigonum submandibulare |
| TA98 | A01.2.02.003 |
| TA2 | 232 |
| FMA | 57779 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
The submandibular triangle (or submaxillary or digastric triangle) corresponds to the region of the neck immediately beneath the body of the mandible.
YouTube Encyclopedic
-
1/3Views:14 46584 44427 345
-
Submandibular Region
-
Triangles of the neck
-
Gross Anatomy: Submandibular, submental and carotid triangles
Transcription
Boundaries and coverings
It is bounded:[1]
- above, by the lower border of the body of the mandible, and a line drawn from its angle to the mastoid process;
- below, by the posterior belly of the Digastricus; in front, by the anterior belly of the Digastricus.
It is covered by the integument, superficial fascia, Platysma, and deep fascia, ramifying in which are branches of the facial nerve and ascending filaments of the cutaneous cervical nerve.
Its floor is formed by the Mylohyoideus anteriorly, and by the hyoglossus posteriorly.
Triangles
Divisions
It is divided into an anterior and a posterior part by the stylomandibular ligament.[citation needed]
Anterior part
The anterior part contains the submandibular gland, superficial to which is the anterior facial vein, while imbedded in the gland is the facial artery and its glandular branches.
Beneath the gland, on the surface of the Mylohyoideus, are the submental artery and the mylohyoid artery and nerve.
Posterior part
The posterior part of this triangle contains the external carotid artery, ascending deeply in the substance of the parotid gland
This vessel lies here in front of, and superficial to, the external carotid, being crossed by the facial nerve, and gives off in its course the posterior auricular, superficial temporal, and internal maxillary branches: more deeply are the internal carotid, the internal jugular vein, and the vagus nerve, separated from the external carotid by the Styloglossus and Stylopharyngeus, and the hypoglossal nerve
See also
Additional images
-
Anterolateral view of head and neck.
-
The triangles of the neck. (Anterior triangles to the left; posterior triangles to the right. Suprahyoid labeled at left.)
Summary of contents
The following summarizes the important structures found in the submandibular triangle:
- 1. The external and internal carotid artery
- 2. The internal jugular vein
- 3. The deep cervical lymph nodes
- 4. The 10th cranial nerve ( Vagus Nerve )
- 5. The submandibular gland
- 6. The submandibular lymph nodes
- 7. The Facial artery and vein
- 8. The 12th cranial nerve ( Hypoglossal Nerve )
References
![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 564 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 564 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
- ^ Casale, Jarett; Varacallo, Matthew (2022), "Anatomy, Head and Neck, Submandibular Triangle", StatPearls, Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing, PMID 30521254, retrieved 2023-01-19
External links
- lesson5 at The Anatomy Lesson by Wesley Norman (Georgetown University) (necktriangle)
- lesson6 at The Anatomy Lesson by Wesley Norman (Georgetown University)
- Anatomy photo:25:16-0100 at the SUNY Downstate Medical Center
- Anatomy figure: 25:01-01 at Human Anatomy Online, SUNY Downstate Medical Center
- Overview at bcm.edu
- Overview at howard.edu


