A crossover cable connects two devices of the same type, for example DTE-DTE or DCE-DCE, usually connected asymmetrically (DTE-DCE), by a modified cable called a crosslink.[1] Such a distinction between devices was introduced by IBM.
The crossing of wires in a cable or in a connector adaptor allows:
- connecting two devices directly, output of one to input of the other,
- letting two terminal (DTE) devices communicate without an interconnecting hub knot, i.e. PCs,
- linking two or more hubs, switches or routers (DCE) together, possibly to work as one wider device.
In contrast, a straight-through cable uses direct wiring to connect complementary devices, e.g. a PC to a switch.
YouTube Encyclopedic
-
1/3Views:13 0742 755 9738 822
-
Crossover Cable Testing
-
Ethernet Cables, UTP vs STP, Straight vs Crossover, CAT 5,5e,6,7,8 Network Cables
-
Step by Step on how to make Crossover Cable.
Transcription
Concept
Straight-through cables are used for most applications, but crossover cables are required in others.
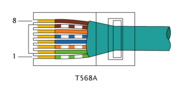
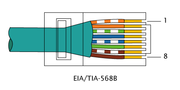
In a straight-through cable, pins on one end correspond exactly to the corresponding pins on the other end (pin 1 to pin 1, pin 2 to pin 2, etc.). Using the same wiring scheme at each end yields a straight-through cable (a given color wire connects to a given number pin, the same at both ends). In this case, the terminations are identical, so only one pinout is required.
In a crossover cable, pins do not correspond – some or all of the conductors are swapped at the terminations. For example, if pin 1 on one end goes to pin 2 on the other end, then pin 2 on one end goes to pin 1 on the other end, and the other pins remain unaffected. Such crossover cables are electrically symmetrical, meaning that they work identically regardless of which way you plug them in (if you turn the cable around, it still connects the same pins as before). Using different wiring at each end yields a crossover cable (a given color wire connects to one number pin at one end, and a different number pin at the other).
Examples

To From |
MDI | MDI-X | Auto MDI-X |
|---|---|---|---|
| MDI | crossover | straight | any |
| MDI-X | straight | crossover | any |
| Auto MDI-X | any | any | any |
- Null modem of RS-232
- Ethernet crossover cable
- Rollover cable
- A loopback is a type of degraded "one side crosslinked connection" connecting a port to itself, usually for test purposes.
Other technologies
Some connection standards use different balanced pairs to transmit data, so crossover cables for them have different configurations to swap the transmit and receive pairs:
- Twisted pair Token Ring uses T568B pairs 1 and 3 (the same as T568A pairs 1 and 2), so a crossover cable to connect two Token Ring interfaces must swap these pairs, connecting pins 4, 5, 3, and 6 to 3, 6, 4, and 5 respectively.
- A T1 cable uses T568B pairs 1 and 2, so to connect two T1 CSU/DSU devices back-to-back requires a crossover cable that swaps these pairs. Specifically, pins 1, 2, 4, and 5 are connected to 4, 5, 1, and 2 respectively.
- A 56K DDS cable uses T568B pairs 2 and 4, so a crossover cable for these devices swaps those pairs (pins 1, 2, 7, and 8 are connected to 7, 8, 1, and 2 respectively).
See also
References
- ^ Dean, Tamara (2010). Network+ Guide to Networks. Delmar. p. 657.