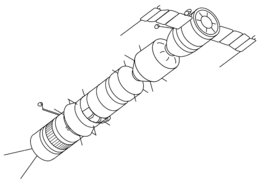
 Soyuz-B (centre) docked with Soyuz 7K-A and Soyuz-V | |
| Manufacturer | OKB-1 |
|---|---|
| Country of origin | Soviet Union |
| Applications | Orbital tug |
| Specifications | |
| Regime | Low Earth Medium Earth Circumlunar |
| Production | |
| Status | Cancelled |
| Launched | None |
Soyuz-B (Russian: Союз-Б meaning Union-B) or Soyuz 9K (Russian: Союз 9К) was a proposed Soviet spacecraft, which was designed for use as an orbital tug. A number of applications were proposed for it, including use as part of the Soyuz A-B-V complex for crewed circumlunar spaceflight.
The Soyuz 9K was intended to have been launched into low Earth orbit by the Soyuz 11A511 carrier rocket. Following launch, it would have been refuelled by up to three Soyuz-V tankers, before commencing its mission. It was primarily intended for use in boosting crewed Soyuz 7K and Soyuz-P spacecraft into higher orbits; the Soyuz-A onto a circumlunar trajectory for human Lunar exploration, and the Soyuz-P into a higher orbit to intercept and destroy another spacecraft.
The Soyuz 9K consisted of two modules: the main spacecraft, and a docking module, NO (Russian: НО). The NO module housed rendezvous and docking systems for the Soyuz-V, as well as equipment for transferring fuel, and additional manoeuvring thrusters. Once the payload spacecraft had docked, the NO would be jettisoned, and the main engine would ignite to propel the Soyuz 9K and its docked payload into a higher orbit.
Following the cancellation of both the Soyuz 7K and P programmes; the former in favour of the LK-1 spacecraft, and the latter in favour of uncrewed anti-satellite programmes, the Soyuz 9K was no longer required, and it too was cancelled.
See also
References
- Wade, Mark. "Soyuz B". Encyclopedia Astronautica. Archived from the original on August 23, 2002. Retrieved 2009-06-30.
- Pike, John. "L-1 Lunar Circumnavigation Mission". GlobalSecurity.org. Retrieved 2009-06-30.



