A hybrid solar eclipse occurred on October 3, 1986. A hybrid eclipse starts and ends as an annular, but is total in the middle around the point of greatest eclipse. Totality occurred for a very short time (calculated at 0.08 seconds) in an area in the Atlantic Ocean, just east of the southern tip of Greenland. The path, on the surface of the Earth, was a narrow, tapered, horse-shoe, and visible only from a thin strip between Iceland and Greenland. At maximum eclipse the solar elevation was about 6°. The path width was just about 800 meters wide.
This eclipse was the last central eclipse of saros 124 and the only hybrid eclipse of that saros.
YouTube Encyclopedic
-
1/5Views:6844 913 9116 372 2603 177 0472 810
-
President Reagan at Ceremony at Queens Park, Grenada on February 20, 1986
-
Christopher Columbus: What Really Happened
-
10 Astronomical Events That Will Happen In Your Lifetime
-
What did the Soviets photograph on Venus? - Real Images!
-
'KTVK-1981 TV 3 News Promo' feat Frank Reynolds, ABC TV News (Phoenix, AZ)
Transcription
Solar Saros 124
This is the eclipse number 53 of Solar Saros 124.
Saros cycle 124, repeating every 18 years, 11 days, containing 73 events. The series started with partial solar eclipse on March 6, 1049. It contains total eclipses from June 12, 1211 through September 22, 1968 with one hybrid solar eclipse on October 3, 1986. The series ends at member 73 as a partial eclipse on May 11, 2347. The longest duration of totality was 5 minutes, 46 seconds on May 3, 1734.
Eclipse date: 3 October 1986
Saros length: 1298 years
Saros duration past: 937 years
Observations
The only witnesses of a few seconds of brief totality were the "Gang of Nine" eclipse chasers aboard a plane at an altitude of 40,000 feet.[1]
The eclipse also resulted in litigation involving a Florida fourth grader whose eyes were allegedly damaged when he viewed the partial eclipse on school grounds. A lower court had dismissed the case on the grounds that the school had no duty to supervise the child after school hours. But the Florida Court of Appeals ruled in 1994 that the jury instruction on that question was improper, and remanded the case.[2]
Related eclipses
Eclipses of 1986
- A partial solar eclipse on April 9.
- A total lunar eclipse on April 24.
- A hybrid solar eclipse on October 3.
- A total lunar eclipse on October 17.
Solar eclipses of 1986–1989
There were 8 solar eclipses between April 9, 1986 and August 31, 1989.
| Solar eclipse series sets from 1986 to 1989 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ascending node | Descending node | |||||
| Saros | Map | Gamma | Saros | Map | Gamma | |
| 119 |  1986 April 9 Partial |
−1.08215 | 124 |  1986 October 3 Hybrid |
0.99305 | |
| 129 |  1987 March 29 Hybrid |
−0.30531 | 134 | 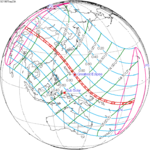 1987 September 23 Annular |
0.27869 | |
| 139 |  1988 March 18 Total |
0.41879 | 144 |  1988 September 11 Annular |
−0.46811 | |
| 149 | 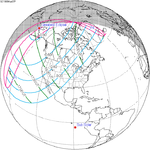 1989 March 7 Partial |
1.09815 | 154 |  1989 August 31 Partial |
−1.19279 | |
Saros 124
Solar saros 124, repeating every about 18 years and 11 days, contains 73 events. The series started with partial solar eclipse on March 6, 1049. It contains total eclipses from June 12, 1211, to September 22, 1968, and a hybrid solar eclipse on October 3, 1986. The series ends at member 73 as a partial eclipse on May 11, 2347. The longest total eclipse occurred on May 3, 1734, at 5 minutes and 46 seconds.[3]
| Series members 43–59 occur between 1801 and 2100: | ||
|---|---|---|
| 43 | 44 | 45 |
 June 16, 1806 |
 June 26, 1824 |
 July 8, 1842 |
| 46 | 47 | 48 |
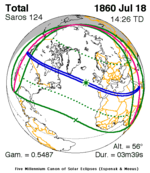 July 18, 1860 |
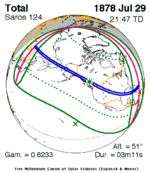 July 29, 1878 |
 August 9, 1896 |
| 49 | 50 | 51 |
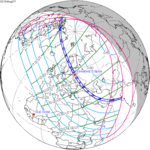 August 21, 1914 |
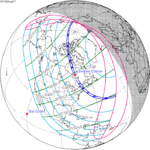 August 31, 1932 |
 September 12, 1950 |
| 52 | 53 | 54 |
 September 22, 1968 |
 October 3, 1986 |
 October 14, 2004 |
| 55 | 56 | 57 |
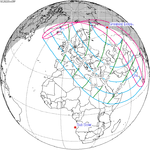 October 25, 2022 |
 November 4, 2040 |
 November 16, 2058 |
| 58 | 59 | |
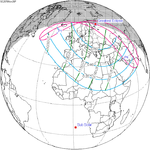 November 26, 2076 |
 December 7, 2094 | |
Metonic cycle
The metonic series repeats eclipses every 19 years (6939.69 days), lasting about 5 cycles. Eclipses occur in nearly the same calendar date. In addition, the octon subseries repeats 1/5 of that or every 3.8 years (1387.94 days). All eclipses in this table occur at the Moon's descending node.
| 21 events between July 22, 1971 and July 22, 2047 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| July 21–22 | May 9–11 | February 26–27 | December 14–15 | October 2–3 |
| 116 | 118 | 120 | 122 | 124 |
 July 22, 1971 |
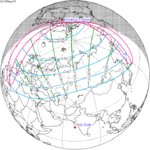 May 11, 1975 |
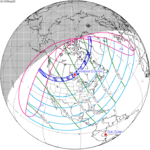 February 26, 1979 |
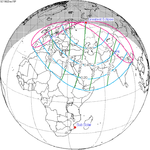 December 15, 1982 |
 October 3, 1986 |
| 126 | 128 | 130 | 132 | 134 |
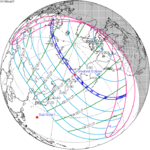 July 22, 1990 |
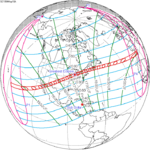 May 10, 1994 |
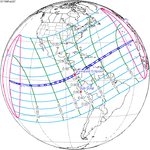 February 26, 1998 |
 December 14, 2001 |
 October 3, 2005 |
| 136 | 138 | 140 | 142 | 144 |
 July 22, 2009 |
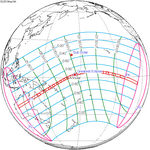 May 10, 2013 |
 February 26, 2017 |
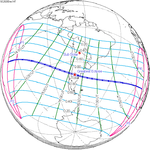 December 14, 2020 |
 October 2, 2024 |
| 146 | 148 | 150 | 152 | 154 |
 July 22, 2028 |
 May 9, 2032 |
 February 27, 2036 |
 December 15, 2039 |
 October 3, 2043 |
| 156 | ||||
 July 22, 2047 | ||||
References
- ^ Schneider, Glenn. "03 October 1986: A Geometrically Remarkable Eclipse".
- ^ Florida Court Reinstates Lawsuit Alleging Eye Damage from Eclipse https://myeclipseglasses.com/litigation.html retrieved 2 Mar. 2023.
- ^ Saros Series Catalog of Solar Eclipses NASA Eclipse Web Site.
- Earth visibility chart and eclipse statistics Eclipse Predictions by Fred Espenak, NASA/GSFC




