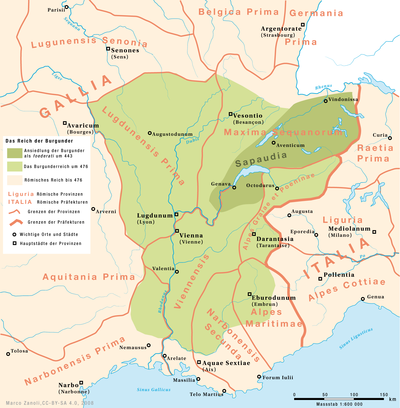
Sapaudia or Sabaudia was an Alpine territory of Late antiquity and the Dark Ages.
Name
The name is a Latinisation of the local words for "forest" or "upland forest", although it is often glossed as "fir" from the roughly similar Latin sapinus.[1] It developed first into Saboia[2] and thence into Italian Savoia (Savoy; French: Savoie, Arpitan: Savouè).[1]
History
Sapaudia first appears[2] in mention by the 4th century late-Roman historian Ammianus Marcellinus,[3] who described it as the southern district of Provincia Maxima Sequanorum, the land of the Sequani enlarged by the Diocletian Reforms. It originally covered the area around Lake Neuchâtel,[1]. Its prefect appeared in the late Roman List of Offices.
During the 5th century, the Burgundians settled in the area, forming the Kingdom of the Burgundians, the capital of which was Geneva. For centuries thereafter, the names Burgundy and Sapaudia/Savoy became closely linked.
In the mid-9th century, Sapaudia was ruled by the Bosonid duke Hucbert as part of the realm of Upper Burgundy. In 933, it was incorporated into Rudolph II's Kingdom of Burgundy.
Humbert I was made count over the area by Rudolph III of Burgundy. For his support of Henry II, Holy Roman Emperor, he received the secular dignities of the bishop of Aosta as its new count following the death of Bishop Anselm. (Anselm's less supportive nephew Burchard was permitted to succeed to the diocese.)
Upon Rudolph's death in 1032, Humbert accepted Conrad II, Holy Roman Emperor's annexation of Arles and supported him in suppressing the revolts of Count Odo and Burchard. For this, he was rewarded with the county of Maurienne (carved out of the diocese of Vienne) and territory in Chablais and the Tarentaise Valley, carved from the diocese of Tarentaise at Moûtiers. This expanded territory became known as the county of Savoy.
See also
- County of Savoy
- Region of Savoy
- French Savoy: Savoie and Haute-Savoie
References
Citations
- ^ a b c Taylor (1896).
- ^ a b Gros (1935).
- ^ Ammianus Marcellinus, 15.11.
Bibliography
- Gros, Adolphe (1935), "Savoy", Dictionnaire Étymologique des Noms de Lieu de la Savoie [An Etymological Dictionary of the Placenames of Savoy], (reprinted by Imprimeries Réunies de Chambéry in 2004), pp. 443 f, ISBN 2-84206-268-X. (in French)
- Taylor, Isaac (1896), "Savoy", Names and Their Histories: Alphabetically arranged as a Handbook of Historical Geography and Topographical Nomenclature, London: Rivington, Percival, & Co.""
