Sterling Alexander Martin Wood | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Nickname(s) | S.A.M. Wood |
| Born | March 17, 1823 Florence, Alabama |
| Died | January 26, 1891 (aged 67) Tuscaloosa, Alabama |
| Place of burial | Evergreen Cemetery, Tuscaloosa, Alabama |
| Allegiance | |
| Service/ | |
| Years of service | 1861–1863 |
| Rank | |
| Commands held | 7th Alabama Infantry Regiment |
| Battles/wars | American Civil War |
| Other work | lawyer, state legislator, university professor |

Sterling Alexander Martin Wood (March 17, 1823 – January 26, 1891) commonly referred to as S.A.M. Wood, was an American lawyer and newspaper editor from Alabama. He served as a Confederate general during the American Civil War until 1863, and resumed practicing law, served as a state legislator, and later taught law.
YouTube Encyclopedic
-
1/3Views:1 30185 421376
-
Ask Sam Series - Exercise without a gym - Health of Australia
-
Fact-Checking Sam Harris 2: Did Jesus Command Christians to Kill in Luke 19:27?
-
Ask Sam Series - Burning belly fat - Health of Australia
Transcription
Early life and career
Wood's father was Alexander Hamilton Wood (1796-1860), a veteran of the War of 1812 and the first mayor of Florence, Alabama. Wood's mother was Mary Ester Evans Wood (1796-1871).[1] Wood was born in Florence, Alabama, in the spring of 1823. He attended St. Joseph's College in Kentucky in 1841, and then moved to Tennessee and became a lawyer there. In 1851 Wood returned to Alabama, where he served in the state legislature.[2] Wood also held the position of "solicitor" of Alabama's fourth judicial court from 1851 to 1857. He was editor of Florence's Gazette newspaper in 1860, during which he actively supported John C. Breckinridge's unsuccessful bid for President of the United States.
Civil War
Early service
Wood chose to follow his home state of Alabama and the Confederate cause, and entered the state forces as a captain in the Alabama state forces as part of the "Florence Guard" on April 3, 1861.[3] He was elected colonel of the 7th Alabama Infantry Regiment on May 18, and Wood and his regiment then served in Pensacola, Florida.[4]
Wood was then given brigade command in the Western Theater in October 1861, joining the Army of Central Kentucky.[2] He was promoted to brigadier general on January 7, 1862.[5] Wood then commanded a brigade in the Army of Mississippi during the Battle of Shiloh in Tennessee on April 6, 1862, and was wounded when his horse dragged him.[2]
Perryville
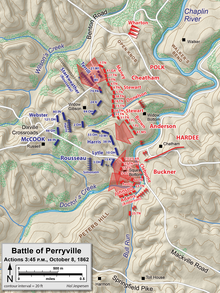
Wood's most notable Confederate service came on October 8, 1862, when he and his brigade fought at Perryville, Kentucky, in the Battle of Perryville. His brigade was part of Maj. Gen. Simon B. Buckner's division in Maj. Gen. William J. Hardee's II Corps and participated in Buckner's attack on a Union position. The Confederates desired to force the Federals back and cut off their escape route at the Dixville Crossroads, effectively surrounding them.
Union infantry and an artillery battery posted on a hill close to the Benton Road shot up Wood's men and forced them back to fall back. Wood reformed his brigade at the base of the hill and renewed the assault. The Federal guns ran low on ammunition and withdrew, and the Confederate attack pushed the Union infantry back towards the crossroads. After the charge Wood's men withdrew and were replaced by Brig. Gen. St. John Richardson Liddell's reserve brigade. In this fight Wood was wounded in the head and would be out of action until November,[2] by which the Army of Mississippi was now called the Army of Tennessee.
Remaining campaigns
Wood resumed command of his brigade on November 20, 1862,[2] and fought in the Army of Tennessee's campaigns during the rest of 1862 and into 1863, including the bloody Battle of Stones River at year's end, throughout the Tullahoma Campaign in the summer of 1863 and the Battle of Chickamauga that September. However Wood resigned his commission on October 17, just prior to the Battles for Chattanooga in November.[2]
Postbellum
Wood resumed his law practice following his resignation from the Confederate Army, and was pardoned by the U.S. Government after the war on November 4, 1865. He then served again in the Alabama Legislature, and was a professor of law at the University of Alabama from 1889 to 1890.[2]
Wood also was the attorney for the Alabama Great Southern Railway from its beginnings in 1877 until his death. In early 1891 at the age of 67, Wood died and was buried in Tuscaloosa, Alabama.[6]
See also
Notes
- ^ Northern Alabama, Historical and Biographical by T.A. Deland and A. Davis Smith, 1988. 1988.
- ^ a b c d e f g Eicher, p. 579.
- ^ Eicher, p. 579; Warner, p. 344.
- ^ Warner, p. 344.
- ^ Wright, p. 68. Appointed from Alabama on January 7, 1862, to rank from that date, and confirmed by Confederate Congress on January 14.
- ^ Warner, p. 345.
References
- Eicher, John H., and David J. Eicher, Civil War High Commands. Stanford: Stanford University Press, 2001. ISBN 978-0-8047-3641-1.
- Sifakis, Stewart. Who Was Who in the Civil War. New York: Facts On File, 1988. ISBN 978-0-8160-1055-4.
- Warner, Ezra J. Generals in Gray: Lives of the Confederate Commanders. Baton Rouge: Louisiana State University Press, 1959. ISBN 978-0-8071-0823-9.
- Wright, Marcus J., General Officers of the Confederate Army: Officers of the Executive Departments of the Confederate States, Members of the Confederate Congress by States. Mattituck, NY: J. M. Carroll & Co., 1983. ISBN 0-8488-0009-5. First published 1911 by Neale Publishing Co.
