| Rübeland Railway | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Overview | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Native name | Rübelandbahn | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Line number |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Locale | Saxony-Anhalt, Germany | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Termini | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Technical | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Line length | 30.3 km (18.8 mi) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Track gauge | 1,435 mm (4 ft 8+1⁄2 in) standard gauge | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electrification | 25 kV AC catenary | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Operating speed | 50 km/h (31.1 mph) (max) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Maximum incline | 6.0% | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||




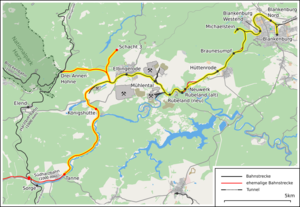
The Rübeland Railway (German: Rübelandbahn) is a railway link from Blankenburg via Rübeland and Königshütte to Tanne in the German state of Saxony-Anhalt. It was built by the Halberstadt-Blankenburg railway (HBE) between 1880 and 1886. The route length is 30.6 kilometres, the height difference over 300 metres. The seven kilometre long section from Königshütte to Tanne was closed in 1968 and the five kilometres from Elbingerode to Königshütte followed suit on 30 August 2000, the last train to Königshütte having run in 1999.
The name Rübeland Railway was first used when the railway was nationalised. Previously it had been known as the Harz Railway (Harzbahn). The line is notable for using 25 kV AC railway electrification, resulting in its use as a railway test track for trains built in Germany that needed to be tested before export.
YouTube Encyclopedic
-
1/2Views:2 9393 546
-
Güterzug in Rübeland [SC]
-
Steam locomotive class 95, DR
Transcription
Route
The Rübeland Railway has a switchback at Michaelstein and several sections with gradients of 6% (1 in 17).
In addition to the junction with the South Harz Railway at Tanne, a branch line from Wechsel to Drei Annen Hohne also linked the Rübeland Railway to the Harzquerbahn and Brocken Railways. This line was closed in 1963 and the track was later lifted, but the trackbed left in place.
History
Since nationalisation
On 1 January 1950 the Halberstadt-Blankenburg Railway, which had been nationalised in 1946, was taken over by the East German Deutsche Reichsbahn.
The Rübeland Railway was electrified between 1960 and 1965 to allow heavier lime traffic from the quarries near Rübeland. Instead of the usual German single-phase electrification system at 15 kV AC and 16 2/3 Hz, single-phase, 25 kV AC 50 Hz power was used, taken from the 110 kV electrical grid via transformers at a substation outside Blankenburg. Although non-standard, the choice of this system did not create any additional operational difficulties, as the Rübeland Railway was not connected to any other electrified lines. Electric operations began on 1 August 1966, with trains being worked by the DR Class E 251, specially built for the line.
The section from Hornberg junction to Königshütte was closed in 2000, goods services having ceased on 2 June 1996 and the last passenger train between Elbingerode and Königshütte having run on 29 May 1999. Traffic was minimal by this time; passenger trains usually consisted of a locomotive and only one or two coaches. The final regular passenger services, between Blankenburg and Elbingerode, were withdrawn by the state of Saxony-Anhalt on 11 December 2005. The section to the Hornberg Lime Works is still worked by goods trains. These trains, with a maximum weight of 600 tonnes uphill and 1,500 tonnes downhill, are top-and-tailed to avoid having to run the locomotive round the train at Michaelstein.
Power to the catenary was switched off on 17 May 2005, and the section from Blankenburg to Elbingerode was put up for lease by DB Netz AG on 12 July 2005. On 1 May 2006 the Fels-Werke company leased the line with an option to purchase. The DB Netz AG handed the line over in working condition to the new operator, Fels Netz GmbH. From that point the Havelländische Eisenbahn (HVLE), who had already paid for most of the goods traffic since 2005, took over the remaining transport operations previously run by Railion. Currently the route is operated by dispatchers (Zugleitbetrieb)(as at 2009). Since 2003 it has been upgraded at a cost of 2.4 million euros, of which 800,000 euros were funded by the state.[2]
Because many people who lived along the line of the Rübeland Railway protested against diesel running due to the noise and exhaust emissions of diesel locomotives, the state of Saxony-Anhalt wanted to fund electrical goods train operations to the tune of 450,000 euros.
In summer 2007 the platforms in Rübeland station were refurbished. The station buildings in Hüttenrode and Königshütte had to be demolished due to their state of disrepair. Hüttenrode station was kept open, the backshunt station at Michaelstein was given new spring-loaded points. In January 2008 the catenary between the Hornberg Lime Works siding and the station of Königshütte was dismantled. The Elbingerode–Hornberg Lime Works section is still worked on demand. In 2008 1.7 million tonnes of lime and limestone were transported.
Re-opening of electrical operations[3]
In 2007 the catenary masts and some of the overhead wire and feeder cables were replaced. As a result, after a two-year break, electric trains are able to run again. Due to a lack of locomotives suitable for steep inclines, the Class 185 was not able to carry out a test run until January 2009 however. Since 18 April 2009, passenger services are also electrified again. The current system is still single-phase AC 25 kV at 50 Hz. Electrification has ensured the operation and preservation of the line for the longer term. The reinstatement of passenger services is now, in principle, possible. In all the upgrade cost 9.6 million euros, of which the state paid 2.4 million.[2]
Current developments
With a view to its longer term (tourist-based) preservation the state has mooted steam services at weekends, although this proposal has difficulties in terms of the likely costs. The last steam locomotive Mammut is still non-operational. It has also been suggested that the Class E 251 (today Class 171) could be used for heritage services. As a result two locomotives have been left at Blankenburg. Because the Rübeland Railway is an inclined route, only locomotives capable of inclined work can work it. On 17 December 2008 the ex-Prussian no. 95 1027 was transferred from Arnstadt shed to the Meiningen Steam Locomotive Works, where it will be made operational for the Rübeland Railway at a cost of 350,000 euros.
Rolling stock
Originally cog locomotives were used on the line, but the introduction of the HBE Animal Class enabled it to be worked with a rack. Following nationalisation, Class 95.0s were also used.
When the line was electrified Class 171s were introduced for passenger and goods trains. From 2000, passenger trains were no longer electric-hauled, because the locomotives had no means of operating the door closing equipment. Push-pull trains were introduced, hauled by Class 218s and running through to Halberstadt. The Class 171 remained in charge of goods trains until 2004. These were, however, replaced by Class 185s and Class 189s; neither lasting very long.
On 1 April 2005, the HVLE delivered two-thirds of the transport services on the Rübeland Railway. They used diesel locomotives of the Blue Tiger class. As a result, DB Cargo also switched to diesel motive power, using Classes 241 and 233, because the maintenance of the catenary was uneconomical. The employment of these classes ended in 2006, when the HVLE took over the remaining Railion services.
Today the following classes are used for goods trains: the Class 346, the Blue Tiger and the Class 285 of the HVLE.
Since the recommencement of electric operations, 185 640 and 641 have worked the line, with the diesels in reserve.
References
- ^ Eisenbahnatlas Deutschland (German railway atlas). Schweers + Wall. 2009. p. 44. ISBN 978-3-89494-139-0.
- ^ a b
Eisenbahnmagazin (in German), no. 6, pp. 23–25, 2009
{{citation}}: Missing or empty|title=(help) - ^ Uwe Behmann: The Rübelndbahn fährt wieder mit 50 Hz. In: Eisenbahn-Revue International 2009, S. 432 - 437.
External links
- The Rübeland Railway (German)
- Rübeland Railway (German)
- The Rübeland Railway 2005 (German)
- Tunnelportale.de/lb/inhalt/Tunnelportale/6864.html Photos of all Tunnel portals, including the closed facilities
