| Posterior auricular artery | |
|---|---|
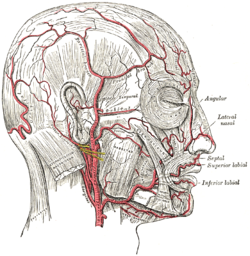 The arteries of the face and scalp. (Posterior auricular visible slightly below ear.) | |
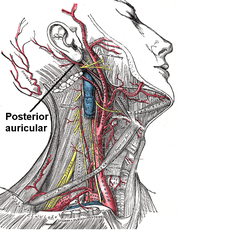 Superficial dissection of the right side of the neck, showing the carotid and subclavian arteries. | |
| Details | |
| Source | external carotid artery |
| Vein | posterior auricular vein |
| Supplies | scalp posterior to the auricle and to the auricle itself |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | arteria auricularis posterior |
| TA98 | A12.2.05.037 |
| TA2 | 4405 |
| FMA | 49624 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
The posterior auricular artery is a small artery that arises from the external carotid artery. It ascends along the side of the head. It supplies several muscles of the neck and several structures of the head.
YouTube Encyclopedic
-
1/3Views:350 48439777 338
-
External Carotid Branches - 3D Anatomy Tutorial
-
MNEMONICS - External Carotid Artery Branches
-
External Carotid & Branches
Transcription
Anatomy
Origin
The artery arises from (the posterior aspect of) the external carotid artery. Its origin occurs immediately superior to the digastric muscle and stylohyoid muscle,[1] and opposite the apex of the styloid process.[citation needed]
Course
The artery passes superior-ward in beneath the parotid gland and styloid process of temporal bone.[1] Next, it courses along a groove between the cartilage of the auricle and the mastoid process. It then divides into its treminal auricular and occipital branches.[1]
Branches and distribution
In the neck, the artery issues branches to the digastric muscle, stylohyoid muscle, sternocleidomastoid muscle, and the parotid gland.[1]
In the neck, the posterior auricular artery issues the stylomastoid artery which enters the stylomastoid foramen to provide arterial supply to the facial nerve (CN VII), tympanic cavity, mastoid air cells of the mastoid antrum, and the semicircular canals.[1]
It issues small branches to the auricle, and supplies blood to the scalp posterior to the auricle. A person may be able to "hear" their own heart rate via this artery, under certain conditions.[citation needed]
See also
Additional images
-
Lateral head anatomy detail
References
- ^ a b c d e Standring, Susan (2020). Gray's Anatomy: The Anatomical Basis of Clinical Practice (42th ed.). New York. pp. 586–587. ISBN 978-0-7020-7707-4. OCLC 1201341621.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link)

