| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
Hydrogen pentacarbonylmanganate(−I) (7CI); Manganese, pentacarbonylhydro- (8CI); Hydridomanganese pentacarbonyl; Hydridopentacarbonylmanganese; Manganese pentacarbonyl hydride; Pentacarbonylhydromanganese; Pentacarbonylmanganese hydride
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
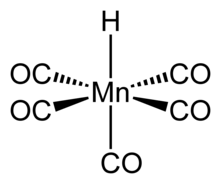
| HMn(CO)5 | |
| Molar mass | 195.99799 g/mol |
| Appearance | At room temperature, it is liquid and colorless. Below its melting point, it may be sublimed in vacuum.[1] |
| Acidity (pKa) | 7.1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Pentacarbonylhydridomanganese is an organometallic compound with formula HMn(CO)5. This compound is one of the most stable "first-row" transition metal hydrides.
YouTube Encyclopedic
-
1/3Views:2 36510 9081 331
-
Metal nitrosyls, their classification and general routes for their preparations (CHE)
-
Metal nitrosyls, their classification and general routes for their preparations (CHE)
-
Effective Atomic Number rule for Organometallic Compounds: EAN rule for Organometallic Compounds
Transcription
Preparation
It was first reported in 1931.[2] Of the several ways to produce this compound,[3] is the protonation of the pentacarbonyl manganate anion. The latter is formed from reduction of dimanganese decacarbonyl, e.g., with superhydride:
- 2 LiHB(C2H5)3 + Mn2(CO)10 → 2 LiMn(CO)5 + H2 + 2 B(C2H5)3
- Li[Mn(CO)5] + CF3SO3H → HMn(CO)5 + CF3SO3Li
Salts of [Mn(CO)
5]−
can be isolated as crystalline PPN+
(μ-nitrido—bis-(triphenylphosphorus)) salt, which is smoothly protonated by CF
3SO
3H.[3]
- PPN[Mn(CO)
5] + CF
3SO
3H → HMn(CO)5 + PPN+
CF
3SO−
3
This compound can also be formed by the hydrolysis of pentacarbonyl(trimethylsilyl)manganese:[4]
- (CO)5MnSiMe3 + H2O → HMn(CO)5 + Me3SiOH (Me = CH3)
Structure and properties
The structure of HMn(CO)5 has been studied by many methods including X-ray diffraction, neutron diffraction, and electron diffraction.[5] HMn(CO)5 can be related to the structure of a hexacarbonyl complex such as Mn(CO)+
6, and therefore has similar properties.[6] The compound has octahedral symmetry[7] and its molecular point group is C4v.[5] The H-Mn bond length is 1.44 ± 0.03 Å.[5] Gas phase electron diffraction analysis confirms these conclusions.
Main reactions
The pKa of HMn(CO)5 in water is 7.1.[8] It is thus comparable to hydrogen sulfide, a common inorganic acid, in its acidity.
A common reaction involving HMn(CO)5 is substitution of the CO ligands by organophosphines, as occurs both thermally and photochemically. In this way the many derivatives form of the type HMn(CO)5-x(PR3)x.[9] (R here need not be a purely hydrocarbon component; it may, for instance, be OEt, where Et = ethyl group.)
HMn(CO)5 can be used to reduce olefins and other organic compounds, as well as metal halides.[3]
It can be methylated with diazomethane.[1]
- HMn(CO)5 + CH2N2 → Mn(CO)5CH3 + N2
Notes
References
- ^ a b Eley, D.D.; Pines, Herman; Weisz, P.B. Advances In Catalysis. 32. 385. ISBN 978-0-12-007832-5
- ^ Hieber, W. Leutert, F. Naturwissenschaften. 1931. 360.
- ^ a b c Hunter, Alan D; Bianconi, Larry J; DiMuzio, Steven J; Braho, Dianne L. Synthesis and Structure- Property Relationships in η6-Arene) Cr(CO)3 Chemistry: From Guided Experiments to Discovery Research. J. Chem. Educ. 75. 1998. 891. doi:10.1021/ed075p891
- ^ Finn, M.G. Pentacarbonyl(trimethylsilyl)manganese. Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis. doi:10.1002/047084289X.rp022s
- ^ a b c Kukolich, S.G. Microwave Spectrum and Molecular Structure for Manganese Pentacarbonyl Hydride. 33. 1994. 1217-1219
- ^ Fenske, Richard. Electronic Structure and Bonding in Manganese Pentacarbonyl Halides and Hydride. Inorganic Chemistry. 9. 1970. 1053-1060.
- ^ Liu, Xian-mei; Wang, Chao-yang; Qian-shu; Xie; Yaoming; King, R. Bruce; Schaefer, Henry F., III. Mononuclear and binuclear manganese carbonyl hydrides. Dalton Trans., 2009, 3774-3785, doi:10.1039/b822913a
- ^ Morris, Robert H. (2016-08-10). "Brønsted–Lowry Acid Strength of Metal Hydride and Dihydrogen Complexes". Chemical Reviews. 116 (15): 8588–8654. doi:10.1021/acs.chemrev.5b00695. hdl:1807/78047. ISSN 0009-2665. PMID 26963836.
- ^ Albertin, Gabriele. Cationic Molecular Hydrogen Complexes of Mn (I). Organometallics. 16. 1997. 4959-4969.
