In chemistry, a parent structure is the structure of an unadorned ion or molecule from which derivatives can be visualized.[1] Parent structures underpin systematic nomenclature and facilitate classification. Fundamental parent structures have one or no functional groups and often have various types of symmetry. Benzene (C6H6) is a chemical itself consisting of a hexagonal ring of carbon atoms with a hydrogen atom attached to each, and is the parent of many derivatives that have substituent atoms or groups replacing one or more of the hydrogens. Some parents are rare or nonexistent themselves, as in the case of porphine, though many simple and complex derivatives are known.
- Porphyrins
-
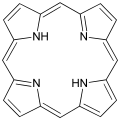
Porphine is the parent of porphyrins.
-
Protoporphyrin IX is a natural derivative of the parent porphine.
-
Octaethylporphyrin is a synthetic derivative of the parent porphine.
YouTube Encyclopedic
-
1/3Views:951 678936 701459 488
-
How To Draw Lewis Structures
-
VSEPR Theory and Molecular Geometry
-
Organic Chemistry Drawing Structures - Bond Line, Skeletal, and Condensed Structural Formulas
Transcription
IUPAC definitions
According to the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry, the concept of parent structure is closely related to or identical to parent compound, parent name, or simply parent.
Organic parents
These species consist of an unbranched chain of skeletal atoms, or consisting of an unsubstituted monocyclic or polycyclic ring system.[2] Parent structures bearing one or more functional groups that are not specifically denoted by a suffix are called functional parents.[3] Names of parent structures are used in IUPAC nomenclature as basis for systematic names.
Hydride parents
A parent hydride is a parent structure with one or more hydrogen atoms. Parent hydrides have a defined standard population of hydrogen atoms attached to a skeletal structure. Parent hydrides are used extensively in organic nomenclature, but are also used in inorganic chemistry.[4]
- Phosphines
-
Phosphine is the parent of phosphines.
-
Phenylphosphine is a derivative of the parent phosphine.
-
3,3′,3′′-Phosphanetriyltris(benzenesulfonic acid) trisodium salt is a derivative of the parent phosphine.
See also
References
- ^ Several examples of parent structures are illustrated in Smith, Michael B.; March, Jerry (2007), Advanced Organic Chemistry: Reactions, Mechanisms, and Structure (6th ed.), New York: Wiley-Interscience, ISBN 978-0-471-72091-1
- ^ Preferred IUPAC Names Provisional Recommendation september 2004 Chapter 1 Par. P-12.1
- ^ Preferred IUPAC Names Provisional Recommendation september 2004; Par. P-34
- ^ Nomenclature of Inorganic Chemistry IUPAC Recommendations 2005 (Red Book) Par. IR-6 Parent Hydride Names and Substitutive Nomenclature - Full text PDF