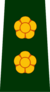
India maintains 10 paramilitary forces.[1]
YouTube Encyclopedic
-
1/5Views:190 92963 868229 49099 46216 275
-
What Are India's Paramilitary Forces? | What Is Central Armed Police Forces? - Explained (Hindi)
-
Decoding the Meaning of Paramilitary Force in India
-
Top 7 Special Forces of India
-
India's Largest Paramilitary Force ? - CAPF #shorts #capf #crpf
-
CAPF & Paramilitary Forces In India | SSB, CRPF, BSF, NSG, CISF, ITBP In Hindi
Transcription
List of paramilitary forces
From 1986 to 2011 the Central Armed Police Forces were considered as Central Police Organisations (CPOs).[2] However, as per their respective acts they all are Armed Police Forces.[3][4]
Ranks and insignia
- Officers
- Personnel below officer rank
| Rank group | Junior commissioned officers | Other ranks | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|

|

|
No insignia | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Subedar Major सूबेदार मेजर |
Subedar सूबेदार |
Naib Subedar नायब सूबेदार |
Warrant officer - |
Havildar[note 10] हवलदार |
Rifleman[note 11] -
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

|

|

|

|
No insignia | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Subedar Major सूबेदार मेजर |
Inspector - |
Sub inspector - |
Assistant Sub inspector - |
Head Constable - |
Naik नायक |
Constable -
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

|

|

|

|
No insignia | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Subedar Major - |
Inspector - |
Sub-inspector - |
Assistant Sub-inspector - |
Head Constable - |
Constable -
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

|

|

|

|
No insignia | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Subedar Major सूबेदार मेजर |
Assistant Commander-1 - |
Assistant Commander-2 - |
Assistant Commander-3 - |
Ranger Grade I - |
Ranger Grade II - |
Combatised tradesmen -
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

|

|

|

|
No insignia | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Subedar Major सूबेदार मेजर |
Inspector - |
Sub inspector - |
Assistant Sub inspector - |
Head Constable - |
Naik नायक |
Lance Naik लांस नायक |
Constable -
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| No insignia | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Subedar Major | Subedar | Naib Subedar | Havildar | Naik | Lance Naik | Sepoy | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rank group | Junior commissioned officers | Other ranks | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
See also
Notes
- ^ Equivalent to the rank Lieutenant general (लेफ्टिनेंट - जनरल)
- ^ Equivalent to the rank Lieutenant general (लेफ्टिनेंट - जनरल)
- ^ Equivalent to the rank Lieutenant general (लेफ्टिनेंट - जनरल)
- ^ Equivalent to the rank Major general (मेजर - जनरल)
- ^ Equivalent to the rank Brigadier (ब्रिगेडियर)
- ^ Equivalent to the rank Colonel (कर्नल)
- ^ Equivalent to the rank Lieutenant colonel (लेफ्टिनेंट - कर्नल)
- ^ Equivalent to the rank Major (मेजर)
- ^ Equivalent to the rank Captain (कप्तान)
- ^ Equivalent to the rank Head constable (-)
- ^ Equivalent to the rank Constable (-)
References
- ^ a b IISS (2012). "Chapter Six: Asia". The Military Balance. 112 (1). London: Routledge: 205–302. doi:10.1080/04597222.2012.663215. S2CID 219626887.
- ^ "Office Memorandum" (PDF). MHA. MHA, GoI. Archived from the original (PDF) on 17 January 2016. Retrieved 26 August 2015.
- ^ "Office Memorandum" (PDF). MHA. MHA, GoI. Archived from the original (PDF) on 17 January 2016. Retrieved 26 August 2015.
- ^ Dholabhai, Nishit (26 March 2011). "For the paramilitary, all's in a new name". The Telegraphy.
- ^ a b c d e "Annual Report 2016-17" (PDF). Ministry of Home Affairs, Government of India. Archived from the original (PDF) on 8 August 2017. Retrieved 12 August 2017.
- ^ Tiwary, Deeptiman (7 December 2021). "Explained: Assam Rifles' dual control structure, and its role". The Indian Express.
- ^ "Introduction". bsf.nic.in. Border Security Force. Retrieved 9 December 2019.
- ^ "Home | Indo Tibetan Border Police, Ministry of Home Affairs". itbpolice.nic.in. Retrieved 9 December 2019.
- ^ a b c (Iiss), The International Institute of Strategic Studies (14 February 2020). The Military Balance 2020. Routledge, Chapman & Hall, Incorporated. ISBN 9780367466398 – via Google Books.
- ^ "Role- SSB Ministry Of Home Affairs, Govt. Of India". ssb.nic.in. Retrieved 9 December 2019.
- ^ Chhina, Man Aman Singh; Kaushik, Krishn (2 September 2020). "Explained: What is the Special Frontier Force, referred to as Vikas Battalion?". The Indian Express. Retrieved 2 September 2020.
- ^ "असम राइफल्स विनियमन 2016 - Assam Rifles Regulation 2016" (PDF). 18 November 2016. Retrieved 20 August 2022.
- ^ "Two Hundred Thirteenth Report - Security Situation in the North Eastern States of India" (PDF). Department-Related Parliamentary Standing Committee on Home Affairs. 19 July 2018. pp. 6–8. Retrieved 21 August 2022.
- ^ a b "All ranks inclusive annual governing body meeting". Central Industrial Security Force. 19 November 2018. Archived from the original on 23 September 2022 – via Facebook.
- ^ a b "The Central Industrial Security Force Act, 1968 (50 of 1968): (As Modified Vide Act No.14 of 1983, 20 of 1989, 40 of 1999 and 22 of 2009)" (PDF). Central Industrial Security Force. 2009. p. 18.
- ^ a b "The Central Reserve Police Force Rules/Regulations/Scheme,1955" (PDF). 24 February 1955.
- ^ a b "Career Prospects". Central Reserve Police Force. Archived from the original on 23 March 2022.
- ^ a b "The National Security Guard Act, 1986 (47 of 1986)" (PDF). Government of India. 22 September 1986. Archived from the original (PDF) on 4 March 2016. Retrieved 23 August 2014.
- ^ a b "Sashastra Seema Bal Rules, 2009" (PDF). Ministry of Home Affairs. 2009.
- ^ "Two Hundred Thirteenth Report - Security Situation in the North Eastern States of India" (PDF). Department-Related Parliamentary Standing Committee on Home Affairs. 19 July 2018. pp. 6–8. Retrieved 21 August 2022.
Further reading
External links
- Assam Rifles official site
- Analysis of the PMF
- An informative article on the PMF
- Global Security article on Border Security Force