In chemistry, an open-chain compound (or open chain compound) or acyclic compound (Greek prefix α 'without' and κύκλος 'cycle') is a compound with a linear structure, rather than a cyclic one.[1] An open-chain compound having no side groups is called a straight-chain compound (also spelled as straight chain compound).[2][3] Many of the simple molecules of organic chemistry, such as the alkanes and alkenes, have both linear and ring isomers, that is, both acyclic and cyclic. For those with 4 or more carbons, the linear forms can have straight-chain or branched-chain isomers. The lowercase prefix n- denotes the straight-chain isomer; for example, n-butane is straight-chain butane, whereas i-butane is isobutane. Cycloalkanes are isomers of alkenes, not of alkanes, because the ring's closure involves a C-C bond. Having no rings (aromatic or otherwise), all open-chain compounds are aliphatic.
Typically in biochemistry, some isomers are more prevalent than others. For example, in living organisms, the open-chain isomer of glucose usually exists only transiently, in small amounts; D-glucose is the usual isomer; and L-glucose is rare.
Straight-chain molecules are often not literally straight, in the sense that their bond angles are often not 180°, but the name reflects that they are schematically straight. For example, the straight-chain alkanes are wavy or "puckered", as the models below show.
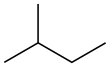
|
||
| branched-chain | straight-chain | cyclic |
| open-chain | ||


YouTube Encyclopedic
-
1/3Views:101 081222 36910 420
-
Converting an open chain monosaccharide into its cyclic structure
-
Classification of Organic Compounds | Organic Chemistry
-
Open Chain and Ring Forms in Monosaccharides
Transcription
References
- ^ IUPAC, Compendium of Chemical Terminology, 2nd ed. (the "Gold Book") (1997). Online corrected version: (2006–) "polycyclic system". doi:10.1351/goldbook.P04724
- ^ Coles, Lydia (1968). "A chromatographic method for the separation of branched-chain and straight-chain compounds of columns containing urea". Journal of Chromatography A. 32 (4): 657–661. doi:10.1016/S0021-9673(01)80544-6. PMID 5645558.
- ^ IUPAC, Compendium of Chemical Terminology, 2nd ed. (the "Gold Book") (1997). Online corrected version: (2006–) "silazanes". doi:10.1351/goldbook.S05669
