| Beijing mouse-eared bat | |
|---|---|
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Chiroptera |
| Family: | Vespertilionidae |
| Genus: | Myotis |
| Species: | M. pequinius
|
| Binomial name | |
| Myotis pequinius Thomas, 1908
| |
| |
The Beijing mouse-eared bat, or Peking myotis (Myotis pequinius) is a species of vesper bat. It is found only in China.
YouTube Encyclopedic
-
1/3Views:15 07165 743673
-
3 Chinese Stocks To Buy (2019/2020)
-
How did cats evolve?
-
Darwin Evolving: Environmental influences on the evolution of communication systems
Transcription
Taxonomy
It was described as a new species in 1908 by British zoologist Oldfield Thomas. The holotype had been collected by Malcolm Playfair Anderson in 1907. Anderson encountered the species in a cave 30 mi (48 km) west of Beijing.[2]
Description
It is a relatively large mouse-eared bat with a forearm length of 48–50 mm (1.9–2.0 in). Its fur is short and velvety, with the fur on its back a gray, reddish-brown. In contrast, its belly fur is off-white.[3]
Biology and ecology
It is insectivorous, consuming mostly beetles.[4] During the day, individuals roost in caves, though they may also roost in human structures.[1]
Range and habitat
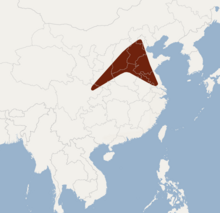
The Beijing mouse-eared bat is endemic to China, where it is found in the provinces of Anhui, Beijing, Henan, Jiangsu, Shanxi, and Sichuan.[1]
Conservation
As of 2019, it is evaluated as a least-concern species by the IUCN. It meets the criteria for this classification because its extent of occurrence exceeds 20,000 km2 (7,700 sq mi); its population is presumably large; and it is unlikely to be experiencing rapid population decline.[1]
See also
References
- ^ a b c d Feng, J.; Jiang, T.L. (2019). "Myotis pequinius". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T14190A22066613. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-3.RLTS.T14190A22066613.en. Retrieved 14 November 2021.
- ^ Thomas, O. (1908). "The Duke of Bedford's Zoological Exploration in Eastern Asia.-X. List of Mammals from the Provinces of Chih-li and Shan-si, N. China". Proceedings of the Zoological Society of London: 637–638.
- ^ Smith, Andrew T.; Xie, Yan; Hoffmann, Robert S.; Lunde, Darrin; MacKinnon, John; Wilson, Don E.; Wozencraft, W. Chris, eds. (2010). A Guide to the Mammals of China. Princeton University Press. p. 379. ISBN 978-1400834112.
- ^ Jones, Gareth; Parsons, Stuart; Zhang, Shuyi; Stadelmann, Benoît; Benda, Petr; Ruedi, Manuel (2006). "Echolocation calls, wing shape, diet and phylogenetic diagnosis of the endemic Chinese bat Myotis pequinius". Acta Chiropterologica. 8 (2): 451–463. doi:10.3161/1733-5329(2006)8[451:ECWSDA]2.0.CO;2.

