| MAPATS | |
|---|---|
 MAPATS missile | |
| Type | Anti-tank guided missile |
| Place of origin | Israel |
| Production history | |
| Manufacturer | Israeli Military Industries |
The MAPATS (man portable anti-tank system, also a Hebrew word for explosion) is a laser guided, beam riding[1] anti-tank guided missile (ATGM) developed by Israel Military Industries as a possible successor to United States' wire-guided missile, BGM-71 TOW. The MAPATS is sometimes nicknamed Hutra (in Hebrew: חוטרא) – an Aramaic word for stick.[2]
The MAPATS can operate day or night, while the gunner must direct a laser designator on the target until missile impact. First revealed in 1984, it has no trailing wire, so it can be fired over water at naval targets or from sea to land, unlike wire-guided ATGMs. The launcher has an elevation ability up to +30°.[3] Externally, the MAPATS is very similar in appearance to the TOW 2.[3]
Versions
The newer version of the MAPATS, developed in the early 1990s, has a new solid-propellant rocket and better laser guidance. Some new warheads were developed by Rafael Advanced Defense Systems, including a tandem-charge high-explosive anti-tank (HEAT), and a high explosive (HE) bunker buster.
Operators
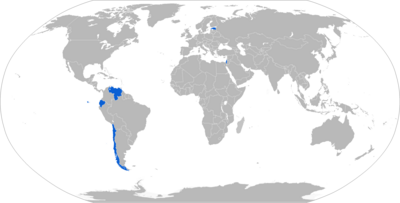
Characteristics
- Effective range: 5,000 meters[1]
- Length: 145 cm[3]
- Caliber: 156 mm[3]
- Weight
- Propulsion: two-stage solid-propellant rocket
- Penetration: 800 mm (original); 1200 mm (tandem-charge)[4]
- Guidance: laser-beam riding[1]
- Warhead: high-explosive anti-tank](HEAT),[3] high explosive (HE)[3]
Comparable systems
References
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j "MAPATS". Deagel.com. Archived from the original on 2016-03-03.
- ^ "Klein Dictionary, חוּטְרָא". www.sefaria.org.
- ^ a b c d e f "IMI MAPATS (Man-Portable Anti-Tank System)". www.militaryfactory.com. Retrieved 2021-04-26.
- ^ "MAPATS Anti-Tank Guided Missile". Military-today.com. Retrieved 2021-04-26.
