In compiler theory, loop interchange is the process of exchanging the order of two iteration variables used by a nested loop. The variable used in the inner loop switches to the outer loop, and vice versa. It is often done to ensure that the elements of a multi-dimensional array are accessed in the order in which they are present in memory, improving locality of reference.
For example, in the code fragment:
for j from 0 to 20
for i from 0 to 10
a[i,j] = i + j
loop interchange would result in:
for i from 0 to 10
for j from 0 to 20
a[i,j] = i + j
On occasion, such a transformation may create opportunities to further optimize, such as automatic vectorization of the array assignments.
YouTube Encyclopedic
-
1/3Views:4 6621 5022 850
-
Loop Interchange - Georgia Tech - HPCA: Part 4
-
Civil3D - Alignment Design for Interchange Loop
-
3 2 6 Reduce Miss Rate by Blocking
Transcription
The utility of loop interchange
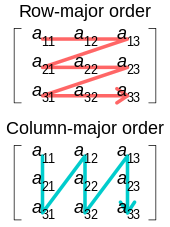
The major purpose of loop interchange is to take advantage of the CPU cache when accessing array elements. When a processor accesses an array element for the first time, it will retrieve an entire block of data from memory to cache. That block is likely to have many more consecutive elements after the first one, so on the next array element access, it will be brought directly from cache (which is faster than getting it from slow main memory). Cache misses occur if the contiguously accessed array elements within the loop come from a different cache block, and loop interchange can help prevent this. The effectiveness of loop interchange depends on and must be considered in light of the cache model used by the underlying hardware and the array model used by the compiler.
In C programming language, array elements in the same row are stored consecutively in memory (a[1,1], a[1,2], a[1,3]) ‒ in row-major order. On the other hand, FORTRAN programs store array elements from the same column together (a[1,1], a[2,1], a[3,1]), using column-major. Thus the order of two iteration variables in the first example is suitable for a C program while the second example is better for FORTRAN.[1] Optimizing compilers can detect the improper ordering by programmers and interchange the order to achieve better cache performance.
Caveat
Loop interchange may lead to worse performance because cache performance is only part of the story. Take the following example:
do i = 1, 10000
do j = 1, 1000
a[i] = a[i] + b[j,i] * c[i]
end do
end do
Loop interchange on this example can improve the cache performance of accessing b(j,i), but it will ruin the reuse of a(i) and c(i) in the inner loop, as it introduces two extra loads (for a(i) and for c(i)) and one extra store (for a(i)) during each iteration. As a result, the overall performance may be degraded after loop interchange.
Safety
It is not always safe to exchange the iteration variables due to dependencies between statements for the order in which they must execute. To determine whether a compiler can safely interchange loops, dependence analysis is required.
See also
References
- ^ "Loop interchange" (PDF). Parallel Programming Guide for HP-UX Systems. HP. August 2003.
Further reading
- Kennedy, Ken; Allen, Randy (2002). Optimizing Compilers for Modern Architectures: A Dependence-Based Approach (2011 digital print of 1st ed.). Academic Press / Morgan Kaufmann Publishers / Elsevier. ISBN 978-1-55860-286-1. LCCN 2001092381.
