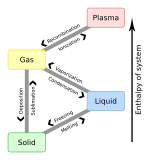
Matter organizes into various phases or states of matter depending on its constituents and external factors like pressure and temperature. In common temperatures and pressures, atoms form the three classical states of matter: solid, liquid and gas. Complex molecules can also form various mesophases such as liquid crystals, which are intermediate between the liquid and solid phases. At high temperatures or strong electromagnetic fields atoms become ionized, forming plasma.
At low temperatures, the electrons of solid materials can also organize into various electronic phases of matter, such as the superconducting state, which is characterized by vanishing resistivity. Magnetic states such as ferromagnetism and antiferromagnetism can also be regarded as phases of matter in which the electronic and nuclear spins organize into different patterns. Such states of matter are studied in condensed matter physics.
In extreme conditions found in some stars and in the early universe, atoms break into their constituents and matter exists as some form of degenerate matter or quark matter. Such states of matter are studied in high-energy physics.
In the 20th century, increased understanding of the properties of matter resulted in the identification of many states of matter. This list includes some notable examples.
YouTube Encyclopedic
-
1/5Views:685 6342 162 3602 824 2423 094 521869 938
-
States of Matter - Solids, Liquids, Gases & Plasma - Chemistry
-
How Many States Of Matter Are There?
-
States of Matter : Solid Liquid Gas
-
States of Matter | #aumsum #kids #science #education #children
-
States Of Matter - Solids, Liquids & Gases | Properties of Matter | Chemistry | FuseSchool
Transcription
Low-energy states of matter
Classical states
- Solid: A solid holds a definite shape and volume and then without the need of a container. The particles are held very close to each other.
- Amorphous solid: A solid in which there is no far-range order of the positions of the atoms.
- Crystalline solid: A solid in which atoms, molecules, or ions are packed in regular order.
- Quasicrystal: A solid in which the positions of the atoms have long-range order, but this is not in a repeating pattern.
- Different structural phases of polymorphic materials are considered to be different states of matter in the Landau theory. For an example, see Ice § Phases.
- Liquid: A mostly non-compressible fluid. Able to conform to the shape of its container but retains a (nearly) constant volume independent of pressure.
- Gas: A compressible fluid. Not only will a gas take the shape of its container but it will also expand to fill the container.
- Mesomorphic states: States of matter intermediate between solid and liquid.
- Plastic crystal: A molecular solid with long-range positional order but with constituent molecules retaining rotational freedom.
- Liquid crystal: Properties intermediate between liquids and crystals. Generally, able to flow like a liquid but exhibiting long-range orientational order.
- Supercritical fluid: At sufficiently high temperatures and pressures, the distinction between liquid and gas disappears.
- Plasma: Unlike gases, which are composed of neutral atoms, plasma contains a significant number of free electrons and ionized atoms. It may self-generate magnetic fields and electric currents and responds strongly and collectively to electromagnetic forces.[1]
Condensates, superfluids and superconductors
- Bose–Einstein condensate: A phase in which a large number of bosons all inhabit the same quantum state, in effect becoming one single wave/particle. This is a low-energy phase that can only be formed in laboratory conditions and at very low temperatures. It must be close to zero kelvin, or absolute zero. Satyendra Nath Bose and Albert Einstein predicted the existence of such a state in the 1920s, but it was not observed until 1995 by Eric Cornell and Carl Wieman.
- Fermionic condensate: Similar to the Bose-Einstein condensate but composed of fermions, also known as Fermi-Dirac condensate. The Pauli exclusion principle prevents fermions from entering the same quantum state, but a pair of fermions can be bound to each other and behave like a boson, and two or more such pairs can occupy quantum states of a given total momentum without restriction.
- Superconductivity: A phenomenon of exactly zero electrical resistance and expulsion of magnetic fields occurring in certain materials when cooled below a characteristic critical temperature. Superconductivity is the ground state of many elemental metals. Superconductors come in multiple varieties:
- Conventional superconductor: A superconductor described by the BCS theory with a singlet order parameter.
- Unconventional superconductor: A superconductor which breaks additional symmetries. For example, d-wave or triplet superconductor, or a Fulde–Ferrell–Larkin–Ovchinnikov superconductor.
- Ferromagnetic superconductor: Materials that display intrinsic coexistence of ferromagnetism and superconductivity.
- Charge-4e superconductor: A proposed state in which electrons are not bound as Cooper pairs but as quadruplets of electrons.
- Superfluid: A phase achieved by a few cryogenic liquids at extreme temperature at which they become able to flow without friction. A superfluid can flow up the side of an open container and down the outside. Placing a superfluid in a spinning container will result in quantized vortices.
- Supersolid: similar to a superfluid, a supersolid can move without friction but retains a rigid shape.
Magnetic states
- Ferromagnetism: A state of matter with spontaneous magnetization.
- Antiferromagnetism: A state of matter in which the neighboring spin are antiparallel with each other, and there is no net magnetization.
- Ferrimagnetism: A state in which local moments partially cancel.
- Altermagnetism: A state with zero net magnetization and spin-split electronic bands.
- Spin-density wave: An ordered state in which spin density is periodically modulated.
- Helimagnetism: A state with spatially rotating magnetic order.
- Spin glass: A magnetic state characterized by randomness.
- Quantum spin liquid: A disordered state in a system of interacting quantum spins which preserves its disorder to very low temperatures, unlike other disordered states.
Electronically ordered states
- Ferroelectricity: A state of matter with spontaneous electric polarization.
- Antiferroelectricity: A state of matter in which the adjacent electric dipoles point in opposite directions.
- Charge ordering
- Charge density wave: An ordered state in which charge density is periodically modulated.
Topological states of matter
- Quantum Hall state: A topological state of matter with quantized Hall resistance.
- Fractional quantum Hall state: A state with fractionally charged quasiparticles. Hall resistance is quantized to fractional multiples of resistance quantum.
- Quantum spin Hall state: a theoretical phase that may pave the way for the development of electronic devices that dissipate less energy and generate less heat. This is a derivative of the quantum Hall state of matter.
- Quantum anomalous Hall state: A state which has a quantized Hall resistance even in the absence of external magnetic field.
- Topological insulator: a material whose interior behaves as an electrical insulator while its surface behaves as an electrical conductor.
- Fractional Chern insulator: A generalization of fractional quantum Hall state to electrons on a lattice.
- Berezinskii-Kosterlitz-Thouless state: A 2D state with unbound vortex-antivortex pairs.
- String-net liquid: Atoms in this state have unstable arrangements, like a liquid, but are still consistent in the overall pattern, like a solid.
- Topological semimetals:[2]
- Topological superconductor[3]
Classification by conductivity
Metallic and insulating states of materials can be considered as different quantum phases of matter connected by a metal-insulator transition. Materials can be classified by the structure of their Fermi surface and zero-temperature dc conductivity as follows:[4]
- Metal:
- Fermi liquid: a metal with well-defined quasiparticle states at the Fermi surface.
- Non-Fermi liquid: Various metallic states with unconventional properties.
- Insulator
- Band insulator: A material that is insulating due to a band gap in its electronic spectrum
- Mott insulator: A material that is insulating due to interactions between electrons.
- Anderson insulator: A material that is insulating due to disorder-induced interference effects.
- Charge-transfer insulators
Miscellaneous states
- Time crystals: A state of matter where an object can have movement even at its lowest energy state.
- Hidden states of matter: Phases that are unattainable or do not exist in thermal equilibrium, but can induced e.g. by photoexcitation.
- Chain-melted state: Metals, such as potassium, at high temperature and pressure, present properties of both a solid and liquid.
- Wigner crystal: a crystalline phase of low-density electrons.
- Hexatic state, a state of matter that is between the solid and the isotropic liquid phases in two dimensional systems of particles.
- Ferroics
- Ferroelastic state, a phenomenon in which a material may exhibit a spontaneous strain.
High energy states
- Degenerate matter: Matter under very high pressure, supported by the Pauli exclusion principle.
- Electron-degenerate matter: Found inside white dwarf stars. Electrons remain bound to atoms but can transfer to adjacent atoms.
- Neutron-degenerate matter: Found in neutron stars. Vast gravitational pressure compresses atoms so strongly that the electrons are forced to combine with protons via inverse beta decay, resulting in a super dense conglomeration of neutrons. (Normally free neutrons outside an atomic nucleus will decay with a half-life of just under fifteen minutes, but in a neutron star, as in the nucleus of an atom, other effects stabilize the neutrons.)
- Strange matter: A type of quark matter that may exist inside some neutron stars close to the Tolman–Oppenheimer–Volkoff limit (approximately 2–3 solar masses). May be stable at lower energy states once formed.
- Quark matter: Hypothetical phases of matter whose degrees of freedom include quarks and gluons
- Color-glass condensate
- Color superconductivity
- Quark–gluon plasma: A phase in which quarks become free and able to move independently (rather than being perpetually bound into particles, or bound to each other in a quantum lock where exerting force adds energy and eventually solidifies into another quark) in an ocean of gluons (subatomic particles that transmit the strong force that binds quarks together). May be briefly attainable in particle accelerators, or possibly inside neutron stars.
- For up to 10−35 seconds after the Big Bang, the energy density of the universe was so high that the four forces of nature – strong, weak, electromagnetic, and gravitational – are thought to have been unified into one single force. The state of matter at this time is unknown. As the universe expanded, the temperature and density dropped and the gravitational force separated, a process called symmetry breaking.
References
- ^ A. Pickover, Clifford (2011). "Plasma". The Physics Book. Sterling. pp. 248–249. ISBN 978-1-4027-7861-2.
- ^ Armitage, N. P.; Mele, E. J.; Vishwanath, Ashvin (2018-01-22). "Weyl and Dirac semimetals in three-dimensional solids". Reviews of Modern Physics. 90 (1): 015001. arXiv:1705.01111. Bibcode:2018RvMP...90a5001A. doi:10.1103/RevModPhys.90.015001.
- ^ Sato, Masatoshi; Ando, Yoichi (2017-07-01). "Topological superconductors: a review". Reports on Progress in Physics. 80 (7): 076501. arXiv:1608.03395. Bibcode:2017RPPh...80g6501S. doi:10.1088/1361-6633/aa6ac7. ISSN 0034-4885. PMID 28367833. S2CID 3900155.
- ^ Imada, Masatoshi; Fujimori, Atsushi; Tokura, Yoshinori (1998-10-01). "Metal-insulator transitions". Reviews of Modern Physics. 70 (4): 1039–1263. Bibcode:1998RvMP...70.1039I. doi:10.1103/RevModPhys.70.1039.