| |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UN number | 1307 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C24H54O3Pt2Si6 | |
| Molar mass | 949.4 g/mol |
| Appearance | colorless solid |
| Density | 1.74 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 12 to 13 °C (54 to 55 °F; 285 to 286 K) |
| Boiling point | 139 °C (282 °F; 412 K) |
| insoluble | |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
  
| |
| Danger | |
| H226, H304, H312, H315, H319, H332, H335, H373 | |
| P210, P260, P280, P301+P310, P305+P351+P338, P370+P378 | |
| Flash point | 86 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
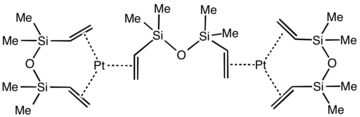
Karstedt's catalyst is an organoplatinum compound derived from divinyl-containing disiloxane. This coordination complex is widely used in hydrosilylation catalysis. It is a colorless solid that is generally assumed to be a mixture of related Pt(0) alkene complexes.[1][2] The catalyst is named after Bruce D. Karstedt, who developed it in the early 1970s while working for General Electric.[3]
Applications
Carbon-silicon bonds are often generated via hydrosilylation of alkenes. This reaction has very important applications to industry. While it is favorable thermodynamically, hydrosilylation does not proceed in the absence of a catalyst, such as Karstedt's catalyst. The catalyst is produced by treatment of chloroplatinic acid by the divinyltetramethyldisiloxane.[4][5]
The catalyst can also be used in a reductive amination reaction between a carboxylic acid and an amine with phenylsilane as the reducing agent.[6]
Structure and bonding
The oxidation state of the platinum is 0. Using X-ray crystallography, the structure of Pt2[(Me2SiCH=CH2)2O]3 has been confirmed. Each Pt(0) center is surrounded by three alkene ligands provided by three 1,1,3,3-tetramethyl-1,3-divinyldisiloxane ligands. The Pt center and six coordinated carbon atoms are approximately coplanar, as found for simpler complexes such as Pt(C2H4)3.[7]
References
- ^ Lewis, Larry N.; Stein, Judith; Gao, Yan; Colborn, Robert E.; Hutchins, Gudrun (1997). "Platinum catalysts used in the silicones industry" (PDF). Platinum Metals Review. 41 (2): 66–74. doi:10.1595/003214097X4126675. S2CID 53707148.
- ^ Stein, Judith; Lewis, L. N.; Gao, Y.; Scott, R. A. (1999). "In Situ Determination of the Active Catalyst in Hydrosilylation Reactions Using Highly Reactive Pt(0) Catalyst Precursors". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 121 (15): 3693–3703. doi:10.1021/ja9825377.
- ^ US Patent 3775452, Bruce D. Karstedt, "Platinum complexes of unsaturated siloxanes and platinum containing organopolysiloxanes", published 1973-11-27, assigned to General Electric
- ^ Richard T. Beresis, Jason S. Solomon, Michael G. Yang, Nareshkumar F. Jain, James S. Panek (1998). "Synthesis of Chiral (E)-Crotylsilanes: [3R- and 3S-]-(4E)-Methyl 3-(Dimethylphenylsilyl)-4-Hexenoate". Organic Syntheses. 75: 78. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.075.0078.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Kohei Tamao; Yoshiki Nakagawa; Yoshihiko Ito (1996). "Regio- and Stereoselective Intramolecular Hydrosilylation of a-hydroxy Enol Ethers: 2,3-syn-2-Methoxymethoxy-1,3-Nonanediol". Organic Syntheses. 73: 94. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.073.0094.
- ^ Sorribes, Iván; Junge, Kathrin; Beller, Matthias (29 September 2014). "Direct Catalytic N-Alkylation of Amines with Carboxylic Acids". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 136 (40): 14314–14319. doi:10.1021/ja5093612. PMID 25230096.
- ^ Hitchcock, Peter B.; Lappert, Michael F.; Warhurst, Nicholas J. W. (1991). "Synthesis and Structure of arac-Tris(divinyldisiloxane) diplatinum(0) Complex and its Reaction with Maleic Anhydride". Angewandte Chemie International Edition in English. 30 (4): 438–440. doi:10.1002/anie.199104381.
