| |||
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
2-Methylprop-1-ene | |||
| Other names
2-Methylpropene
Isobutene γ-Butylene 2-Methylpropylene Methylpropene | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.003.697 | ||
| EC Number |
| ||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| RTECS number |
| ||
| UNII | |||
| UN number | 1055 In Liquefied petroleum gas: 1075 | ||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties[1] | |||
| C4H8 | |||
| Molar mass | 56.106 g/mol | ||
| Appearance | Colorless gas | ||
| Density | 0.5879 g/cm3, liquid | ||
| Melting point | −140.3 °C (−220.5 °F; 132.8 K) | ||
| Boiling point | −6.9 °C (19.6 °F; 266.2 K) | ||
| -44.4·10−6 cm3/mol | |||
| Hazards[2] | |||
| GHS labelling: | |||
 
| |||
| Danger | |||
| H220 | |||
| P210, P377, P381, P403 | |||
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |||
| Flash point | flammable gas | ||
| 465 °C (869 °F; 738 K) | |||
| Explosive limits | 1.8–9.6% | ||
| Related compounds | |||
Related butenes
|
1-Butene cis-2-Butene trans-2-Butene | ||
Related compounds
|
Isobutane | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
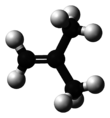
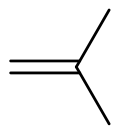
Isobutylene (or 2-methylpropene) is a hydrocarbon with the chemical formula (CH3)2C=CH2. It is a four-carbon branched alkene (olefin), one of the four isomers of butylene. It is a colorless flammable gas, and is of considerable industrial value.[3]
YouTube Encyclopedic
-
1/5Views:1 2792 34039 81167 42871 747
-
Make Isobutylene
-
How to Write the Structure for Isobutylene
-
Chlorination of Isobutene: 1-MCP ep02
-
Chlorination of Isobutene: The Gas Phase! 1-MCP ep02.2
-
Chlorination of Isobutene: Attempt 3! 1-MCP ep02.3
Transcription
Production
Polymer and chemical grade isobutylene is typically obtained by dehydrating tertiary butyl alcohol (TBA) or catalytic dehydrogenation of isobutane (Catofin or similar processes).[4] Gasoline additives methyl tert-butyl ether (MTBE) and ethyl tert-butyl ether (ETBE), respectively, are produced by reacting methanol or ethanol with isobutylene contained in butene streams from olefin steam crackers or refineries, or with isobutylene from dehydrated TBA. Isobutylene is not isolated from the olefin or refinery butene stream before the reaction, as separating the ethers from the remaining butenes is simpler. Isobutylene can also be produced in high purities by "back-cracking" MTBE or ETBE at high temperatures and then separating the isobutylene by distillation from methanol.
Isobutylene is a byproduct in the ethenolysis of diisobutylene to prepare neohexene:[5]
- (CH3)3C-CH=C(CH3)2 + CH2=CH2 → (CH3)3C-CH=CH2 + (CH3)2C=CH2
Uses
Isobutylene is used in the production of a variety of products. It is alkylated with butane to produce isooctane or dimerized to diisobutylene (DIB) and then hydrogenated to make isooctane, a fuel additive. Isobutylene is also used in the production of methacrolein. Polymerization of isobutylene produces butyl rubber (polyisobutylene or PIB). Antioxidants such as butylated hydroxytoluene (BHT) and butylated hydroxyanisole (BHA) are produced by Friedel-Crafts alkylation of phenols with isobutylene.
tert-Butylamine is produced commercially by amination of isobutylene using zeolite catalysts:[6]
- NH3 + CH2=C(CH3)2 → H2NC(CH3)3
Applications are found in the calibration of photoionization detectors.
Safety
Isobutylene is a highly flammable gas.
See also
References
- ^ The Merck Index: An Encyclopedia of Chemicals, Drugs, and Biologicals (11th ed.), Merck, 1989, ISBN 091191028X, 5024.
- ^ Isobutene, International Chemical Safety Card 1027, Geneva: International Programme on Chemical Safety, April 2000
- ^ Geilen, Frank M.A.; Stochniol, Guido; Peitz, Stephan; Schulte-Koerne, Ekkehard (2014). "Butenes". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a04_483.pub3. ISBN 978-3527306732.
- ^ Olah, George A.; Molnár, Árpád (May 2003), Hydrocarbon Chemistry, Wiley-Interscience, ISBN 978-0-471-41782-8.
- ^ Lionel Delaude; Alfred F. Noels. "Metathesis". Kirk-Othmer Encyclopedia of Chemical Technology. Wiley.
- ^ Eller, Karsten; Henkes, Erhard; Rossbacher, Roland; Höke, Hartmut (2000). "Amines, Aliphatic". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a02_001. ISBN 978-3527306732.
External links
- International Chemical Safety Card 1027
- SIDS Initial Assessment Report for Isobutylene from the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD)