| Internal carotid plexus | |
|---|---|
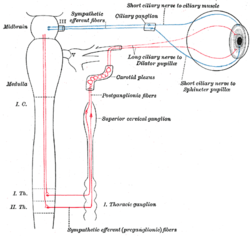 Sympathetic connections of the ciliary and superior cervical ganglia. (Carotid plexus visible center top.) Note that the label "Sympathetic Efferent Fibres" above the nerves arising in the midbrain is an error. This label should read "Parasympathetic Efferent Fibres" as the sphincter pupillæ and ciliary muscle are innervated only by parasympathetic fibres. | |
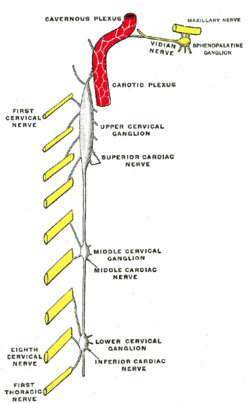 Diagram of the cervical sympathetic. (Carotid plexus visible center top.) | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | plexus caroticus internus |
| TA98 | A14.3.03.004 |
| TA2 | 6645 |
| FMA | 67533 |
| Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy | |

The internal carotid plexus is a nerve plexus situated upon the lateral side of the internal carotid artery. It is composed of post-ganglionic sympathetic fibres which have synapsed at (i.e. have their nerve cell bodies at) the superior cervical ganglion. The plexus gives rise to the deep petrosal nerve.[1]
YouTube Encyclopedic
-
1/3Views:24 218573 769350 484
-
Choroid plexus (plexus choroideus) - Human Anatomy | Kenhub
-
Circle of Willis - 3D Anatomy Tutorial
-
External Carotid Branches - 3D Anatomy Tutorial
Transcription
Anatomy
Postganglionic sympathetic fibres ascend from the superior cervical ganglion, along the walls of the internal carotid artery, to enter the internal carotid plexus. These fibres are then distributed to deep structures, including the superior tarsal muscle and pupillary dilator muscle.[2] It includes fibres destined for the pupillary dilator muscle as part of a neural circuit regulating pupillary dilatation component of the pupillary reflex.[3] Some fibres of the plexus converge to form the deep petrosal nerve.[4]
The internal carotid plexus communicates with the trigeminal ganglion, the abducent nerve, and the pterygopalatine ganglion (also named sphenopalatine); it distributes filaments to the wall of the internal carotid artery, and also communicates with the tympanic branch of the glossopharyngeal nerve.[citation needed]
The plexus there occasionally presents a small gangliform swelling - the carotid ganglion - on the under surface of the artery.[citation needed]
Additional images
-
Nerves of the orbit, and the ciliary ganglion. Side view.
-
Pathways in the Ciliary Ganglion.
References
![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 977 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 977 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
- Notes
- ^ Goosmann, Madeline M.; Dalvin, Mark (2023), "Anatomy, Head and Neck, Deep Petrosal Nerve", StatPearls, Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing, PMID 30521238, retrieved 2023-07-31
- ^ Hal Blumenfeld, "Neuroanatomy through Clinical Cases", Sinauer Associates, 2002, p543
- ^ Patestas, Maria A.; Gartner, Leslie P. (2016). A Textbook of Neuroanatomy (2nd ed.). Hoboken, New Jersey: Wiley-Blackwell. p. 367. ISBN 978-1-118-67746-9.
- ^ Richard L. Drake, Wayne Vogel & Adam W M Mitchell, "Gray's Anatomy for Students", Elsevier inc., 2005


