A hyperbolic tree (often shortened as hypertree) is an information visualization and graph drawing method inspired by hyperbolic geometry.

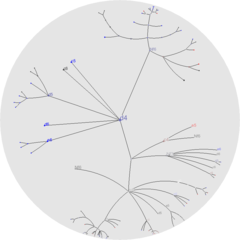
Displaying hierarchical data as a tree suffers from visual clutter as the number of nodes per level can grow exponentially. For a simple binary tree, the maximum number of nodes at a level n is 2n, while the number of nodes for trees with more branching grows much more quickly. Drawing the tree as a node-link diagram thus requires exponential amounts of space to be displayed.
One approach is to use a hyperbolic tree, first introduced by Lamping et al.[1] Hyperbolic trees employ hyperbolic space, which intrinsically has "more room" than Euclidean space. For instance, linearly increasing the radius of a circle in Euclidean space increases its circumference linearly, while the same circle in hyperbolic space would have its circumference increase exponentially. Exploiting this property allows laying out the tree in hyperbolic space in an uncluttered manner: placing a node far enough from its parent gives the node almost the same amount of space as its parent for laying out its own children.
Displaying a hyperbolic tree commonly utilizes the Poincaré disk model of hyperbolic geometry, though the Klein-Beltrami model can also be used. Both display the entire hyperbolic plane within a unit disk, making the entire tree visible at once. The unit disk gives a fish-eye lens view of the plane, giving more emphasis to nodes which are in focus and displaying nodes further out of focus closer to the boundary of the disk. Traversing the hyperbolic tree requires Möbius transformations of the space, bringing new nodes into focus and moving higher levels of the hierarchy out of view.
Hyperbolic trees were patented in the U.S. by Xerox in 1996, but the patent has since expired.[2]
YouTube Encyclopedic
-
1/3Views:1 0253 514564
-
Hyperbolic Slot (Kannada)
-
Interactive Visualization of Genealogical Graphs
-
Sample
Transcription
See also
- Hyperbolic geometry
- Binary tiling
- Information visualization
- Radial tree – is also circular, but uses linear geometry.
- Tree (data structure)
- Tree (graph theory)
References
- ^ Lamping, John Ogden; Rao, Ramana; Pirolli, Peter (May 1995). A focus+context technique based on hyperbolic geometry for visualizing large hierarchies. Proceedings of the ACM Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems (CHI 1995). pp. 401–408. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.20.1530. doi:10.1145/223904.223956. Archived from the original on 2017-05-10. Retrieved 2021-04-13.
- ^ US patent 5590250, Lamping; John O. & Rao; Ramana B., "Layout of node-link structures in space with negative curvature", assigned to Xerox Corporation
External links
- d3-hypertree – HTML5 Hyperbolic tree implementation, MIT licensed
- Hyperbolic Tree of life – Open source tree of life visualisation using Open Tree of Life data set
- The Green Tree of Life – Tree of life – University of California at Berkeley and Jepson Herbaria
- Tree of life Similar to the above, but with pictures
- RogueViz supports hyperbolic trees.
