| Hohenlohisch | |
|---|---|
| Native to | North-east Baden-Württemberg |
| Latin (German alphabet) | |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-3 | – |
| Glottolog | None |
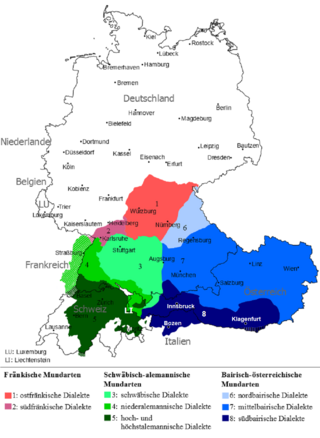 Map showing East Franconian dialects in red. | |
Hohenlohisch is an East Franconian dialect spoken principally in north-eastern Baden-Württemberg in Germany, and which also overlaps dialects on the Bavarian border. It is spoken in Landkreis Schwäbisch Hall, Hohenlohekreis and what was formerly the Bad Mergentheim Landkreis (now in the Main-Tauber-Kreis), although the latter has recently been assumed into the Tauber-Franconian dialect group.[1]
Origin of name
The name Hohenlohisch comes from the aristocratic Hohenlohe dynasty, which divided into a number of branches, and the name of their Imperial State. Two branches of the family were raised to the rank of principalities of the Holy Roman Empire in 1744 and 1764 respectively; in 1806 they lost their independence and their lands became part of the Kingdoms of Bavaria (Hohenlohe-Schillingsfürst) and of Württemberg. At the time of the Confederation of the Rhine in 1806, the area of Hohenlohe was 1 760 km² and its estimated population was 108,000.[2] In the course of time the dialect came to be called Hohenlohisch.
Notable writers in the dialect
- Dramatist and lyricist Gottlob Haag (1926–2008) from Wildentierbach, Niederstetten.
Music in the dialect
- Annâweech[3]
References
- ^ Alfred Kuppler: Hohenlohisch soll nicht sterben!. Hohenloher Druck- und Verlagshaus, Gerabronn und Crailsheim 1988, ISBN 3-87354-168-8
- ^ Online map showing Hohenlohe in 1789
- ^ "Annaweech - Lieaderlich, iwwerzwerch unn meeh". Retrieved 7 November 2022.
- Erwin Strasser: Tausend Worte Hohenlohisch. W. Eppe Verlag, Bergatreute 1988, ISBN 3-89089-209-4
- Eberhard Zanzinger: Hohenloher Ausdrücke und Redensarten. Verlag Robert Baier, Crailsheim 2004, ISBN 3-92923-332-0
External links
- "Hohenlohisch-German dictionary". Archived from the original on 5 September 2019.
