| Hindbrain | |
|---|---|
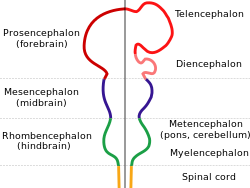 | |
 Scheme of the roof of the fourth ventricle. | |
| Identifiers | |
| MeSH | D012249 |
| NeuroNames | 540 |
| NeuroLex ID | birnlex_942 |
| TA98 | A14.1.03.002 |
| FMA | 67687 |
| Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy | |
The hindbrain, rhombencephalon or lower brain[1] is a developmental categorization of portions of the central nervous system in vertebrates. It includes the medulla, pons, and cerebellum. Together they support vital bodily processes.[2]
YouTube Encyclopedic
-
1/5Views:10 1645 0365 0035 570311 266
-
[ CNS INTRO ] Brain Parts And Functions [ Forebrain Midbrain Hindbrain ]
-
Parts of the Brain: Hindbrain Structures (Intro Psych Tutorial #32)
-
Central Nervous System (Hindbrain) - Control and Coordination | Class 10 Biology
-
Hindbrain
-
Brain: Parts & functions (Fore, mid & hind) | Control & Coordination | Biology | Khan Academy
Transcription
Metencephalon
Rhombomeres Rh3-Rh1 form the metencephalon.
The metencephalon is composed of the pons and the cerebellum; it contains:
- a portion of the fourth (IV) ventricle,
- the trigeminal nerve (CN V),
- abducens nerve (CN VI),
- facial nerve (CN VII),
- and a portion of the vestibulocochlear nerve (CN VIII).
Myelencephalon
Rhombomeres Rh8-Rh4 form the myelencephalon.
The myelencephalon forms the medulla oblongata in the adult brain; it contains:
- a portion of the fourth ventricle,
- the glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX),
- vagus nerve (CN X),
- accessory nerve (CN XI),
- hypoglossal nerve (CN XII),
- and a portion of the vestibulocochlear nerve (CN VIII).
Evolution
The hindbrain is homologous to a part of the arthropod brain known as the sub-oesophageal ganglion, in terms of the genes that it expresses and its position in between the brain and the nerve cord.[3] It has been suggested that the hindbrain first evolved in the urbilaterian—the last common ancestor of chordates and arthropods—between 570 and 555 million years ago.[3][4]
Hindbrain diseases
A rare brain disease of the cerebellum is rhombencephalosynapsis characterized by an absent or partially formed vermis. Symptoms can include truncal ataxia. The disorder is a main feature of Gomez-Lopez-Hernandez syndrome.
References
- ^ "Brain: Parts & functions (Fore, mid & hind)". Khan Academy. Retrieved 5 September 2022.
- ^ "Brain atlas - Hindbrain". Brain explorer. Lundbeck Institute. Archived from the original on April 10, 2015. Retrieved June 8, 2015.
- ^ a b Ghysen, Alain (1 December 2003). "The origin and evolution of the nervous system". International Journal of Developmental Biology. 47 (7–8): 555–562. PMID 14756331.
- ^ Haycock, Daniel E. (2011). Being and Perceiving. Manupod Press. p. 41. ISBN 978-0-9569621-0-2.
Further reading
- Ishak, Gisele E.; Dempsey, Jennifer C.; Shaw, Dennis W. W.; Tully, Hannah; Adam, Margaret P.; Sanchez-Lara, Pedro A.; Glass, Ian; Rue, Tessa C.; Millen, Kathleen J.; Dobyns, William B.; Doherty, Dan (May 2012). "Rhombencephalosynapsis: a hindbrain malformation associated with incomplete separation of midbrain and forebrain, hydrocephalus and a broad spectrum of severity". Brain. 135 (5): 1370–1386. doi:10.1093/brain/aws065. PMC 3338925. PMID 22451504.
- Tully, Hannah M.; Dempsey, Jennifer C.; Ishak, Gisele E.; Adam, Margaret P.; Mink, Jonathan W.; Dobyns, William B.; Gospe, Sidney M.; Weiss, Avery; Phillips, James O.; Doherty, Dan (December 2013). "Persistent figure-eight and side-to-side head shaking is a marker for rhombencephalosynapsis: Persistent Head Shaking". Movement Disorders. 28 (14): 2019–2023. doi:10.1002/mds.25634. PMC 5510988. PMID 24105968.
- Poretti, Andrea; Alber, Fabienne Dietrich; Bürki, Sarah; Toelle, Sandra P.; Boltshauser, Eugen (January 2009). "Cognitive outcome in children with rhombencephalosynapsis". European Journal of Paediatric Neurology. 13 (1): 28–33. doi:10.1016/j.ejpn.2008.02.005. PMID 18407532.
- Bell, B; Stanko, H; Levine, R (July 2005). "Normal IQ in a 55-year-old with newly diagnosed rhombencephalosynapsis". Archives of Clinical Neuropsychology. 20 (5): 613–621. doi:10.1016/j.acn.2005.02.003. PMID 15905069.
- Paprocka, Justyna; Jamroz, Ewa; Ścieszka, Ewa; Kluczewska, Ewa (2012). "Isolated rhomboencephalosynapsis – a rare cerebellar anomaly". Polish Journal of Radiology. 77 (1): 47–49. doi:10.12659/PJR.882587. PMC 3389961. PMID 22802865.
