
A fractal curve is, loosely, a mathematical curve whose shape retains the same general pattern of irregularity, regardless of how high it is magnified, that is, its graph takes the form of a fractal.[1] In general, fractal curves are nowhere rectifiable curves — that is, they do not have finite length — and every subarc longer than a single point has infinite length.[2]
A famous example is the boundary of the Mandelbrot set.
Fractal curves in nature
Fractal curves and fractal patterns are widespread, in nature, found in such places as broccoli, snowflakes, feet of geckos, frost crystals, and lightning bolts.[3][4][5][6]
See also Romanesco broccoli, dendrite crystal, trees, fractals, Hofstadter's butterfly, Lichtenberg figure, and self-organized criticality.
Dimensions of a fractal curve
Most of us are used to mathematical curves having dimension one, but as a general rule, fractal curves have different dimensions,[7] also see fractal dimension and list of fractals by Hausdorff dimension.
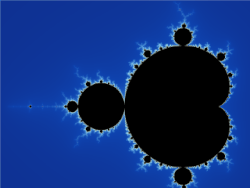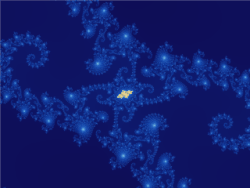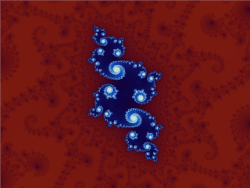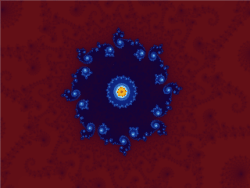
Relationships of fractal curves to other fields
Starting in the 1950s Benoit Mandelbrot and others have studied self-similarity of fractal curves, and have applied theory of fractals to modelling natural phenomena. Self-similarity occurs, and analysis of these patterns has found fractal curves in such diverse fields as
As examples, "landscapes" revealed by microscopic views of surfaces in connection with Brownian motion, vascular networks, and shapes of polymer molecules all relate to fractal curves.[1]
Examples
See also
References
- ^ a b "Geometric and topological recreations".
- ^ Ritzenthaler, Chella. "Fractal Curves" (PDF).
- ^ McNally, Jess. "Earth's Most Stunning Natural Fractal Patterns". Wired. wired.com. Retrieved 17 May 2020.
- ^ Tennenhouse, Erica (July 5, 2016). "8 Stunning Fractals Found in Nature".
- ^ LaMonica, Martin (March 30, 2017). "Fractal patterns in nature and art are aesthetically pleasing and stress-reducing".
- ^ Gunther, Shea (April 24, 2013). "14 amazing fractals found in nature". Retrieved 2020-05-17.
- ^ Bogomolny, Alexander. "Fractal Curves and Dimension". cut-the-knot.
External links
- Wolfram math on fractal curves
- The Fractal Foundation's homepage
- fractalcurves.com
- Making a Kock Snowflake, from Khan Academy
- Area of a Koch Snowflake, from Khan Academy
- Youtube on space-filling curves
- Youtube on the Dragon Curve
