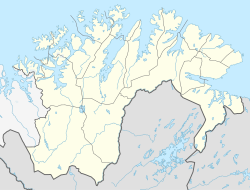
Finnmarksvidda
Finnmárkkoduottar (Northern Sami) | |
|---|---|
 The lowest elevations can be found in the eastern part of Finnmarksvidda, near Karasjok and Tana. River valleys in the area are only 100–250 m (300–800 ft) above sea level. | |
| Coordinates: 69°19′N 23°49′E / 69.317°N 23.817°E | |
| Location | Finnmark, Norway |
| Native name | Finnmárkkoduottar (Northern Sami) |
| Area | |
| • Total | 22,000 km2 (8,500 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 300 to 500 m (980 to 1,640 ft) |
Finnmarksvidda (Northern Sami: Finnmárkkoduottar; English: Finnmark plateau/highland) is Norway's largest plateau, with an area greater than 22,000 square kilometres (8,500 sq mi).[1] The plateau lies about 300 to 500 metres (980 to 1,640 ft) above sea level. Approximately 36% of Finnmark lies on the Finnmarksvidda.
YouTube Encyclopedic
-
1/2Views:347775
-
Lofoten folkehøgskole, vintertur over Finnmarksvidda
-
Webinar - Finnmarksvidda på ski med Atle Trodal
Transcription
Geography

From Alta Municipality in the west to the Varanger Peninsula in the east it stretches for approximately 300 kilometres (190 mi), being at least that wide from north to south, extending into Finland. The southeastern part of the plateau is protected by the Anárjohka National Park. The 1,409 square kilometres (544 sq mi) park opened in 1976.[2]
Some circular lakes in Finnmarksvidda may be remnants of collapsed pingos that developed during cold periods of the last deglaciation.[3]
Fauna and flora
The plateau includes extensive birch woods, pine barrens, bogs, and glacially formed lakes. Finnmarksvidda is situated north of the Arctic Circle and is best known as the land of the once nomadic Sami people and their reindeer herds. Their shelters in the tundra are still used in the winter time.
Climate

Finnmarksvidda, located in the interior of the county has a subarctic climate with the coldest winter temperatures in Norway: the coldest temperature ever recorded was −51.4 °C (−60.5 °F) in Karasjok on 1 January 1886. The climate of Kautokeino (307 m) represents the climate of the plateau.
References
- ^ "About Finnmark". Turistforeningen. Archived from the original on 2010-11-24. Retrieved 2010-04-10.
- ^ Ryvarden, Leif (2007). Stabbursdalen, Øvre Pasvik og Øvre Anárjohka. Norges nasjonalparker (in Norwegian). Vol. 3. Gyldendal. ISBN 9788205376380.
- ^ Svensson, Harald (1976). "Pingo problems in the Scandinavian countries". Biuletyn Peryglacjalny. 26: 33–40.