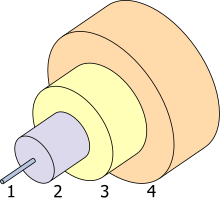
1. Core 9 μm diameter
2. Cladding 125 μm dia.
3. Coating 250 μm dia.
4. Buffer or jacket 900 μm dia.

The core of a conventional optical fiber is the part of the fiber that guides the light. It is a cylinder of glass or plastic that runs along the fiber's length.[1] The core is surrounded by a medium with a lower index of refraction, typically a cladding of a different glass, or plastic. Light travelling in the core reflects from the core-cladding boundary due to total internal reflection, as long as the angle between the light and the boundary is greater than the critical angle. As a result, the fiber transmits all rays that enter the fiber with a sufficiently small angle to the fiber's axis. The limiting angle is called the acceptance angle, and the rays that are confined by the core/cladding boundary are called guided rays.
The core is characterized by its diameter or cross-sectional area. In most cases the core's cross-section should be circular, but the diameter is more rigorously defined as the average of the diameters of the smallest circle that can be circumscribed about the core-cladding boundary, and the largest circle that can be inscribed within the core-cladding boundary. This allows for deviations from circularity due to manufacturing variation.
Another commonly quoted statistic for core size is the mode field diameter. This is the diameter at which the intensity of light in the fiber falls to some specified fraction of maximum (usually 1/e2 ≈ 13.5%). For single-mode fiber, the mode field diameter is larger than the physical diameter of the core, because the light penetrates slightly into the cladding as an evanescent wave.
The three most common core sizes are:
- 9 μm diameter (single-mode)
- 50 μm diameter (multi-mode)
- 62.5 μm diameter (multi-mode)[2]
YouTube Encyclopedic
-
1/3Views:107 52794 60343 218
-
Optical Fibres
-
What is Fiber Optics? | Mocomi Kids
-
Fiber Optic Cable: Part 6 - Armored Cable
Transcription
See also
References
- ^ Insulation/circuits. Lake Publishing Corporation. 1978.
- ^ "The FOA Reference For Fiber Optics - Optical Fiber". www.thefoa.org. Retrieved April 10, 2016.
