| Unique-headed bugs Temporal range:
| |
|---|---|
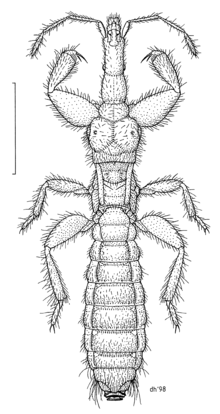
| |
| Phthirocoris magnus female | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Arthropoda |
| Class: | Insecta |
| Order: | Hemiptera |
| Suborder: | Heteroptera |
| Superfamily: | Enicocephaloidea |
| Family: | Enicocephalidae Stål, 1860 |
Enicocephalidae, also called unique-headed bugs and gnat bugs, are a family of around 300 species of the suborder Heteroptera. They are typically 4 mm (0.16 in) long, and found throughout the world. They have an elongated head, constricted in places, hence their head is 'unique'.

They are classified into about 47 genera placed in five subfamilies. The family members can be separated from those of the Aenictopecheidae on the basis of the pronotal division into three lobes (except in the genus Alienates). They also show polymorphism with winged males and wingless or short-winged females.[1]
YouTube Encyclopedic
-
1/5Views:52724 2291 8182 9461 205
-
Enicocephalidae - Ancient Assasin Bug in Amber
-
Baltic Amber - Explained
-
Ancient cretaceous forest remains in amber
-
Rare museum grade pieces of burmite amber - Inclusiopedia
-
Cretapsara Athanata - first 100milion years old crab discovered in Amber
Transcription
Genera
Genera in the family include:
- Alienates Barber, 1953 i c g
- Boreostolus Wygodzinsky and Stys, 1970 i c g
- Brevidorsus Kritsky, 1977 i c g
- Ciucephalus Štys, 1982 g
- Disphaerocephalus Cockerell, 1917 g
- Enicocephalinus Azar, Fleck, Nel & Solignac, 1999 g
- Enicocephalus Westwood, 1838 g
- Gourlayocoris c g
- Henicocephalus g
- Henschiella Horvath, 1888 g
- Hoplitocoris Jeannel, 1942 g
- Hymenocoris Uhler, 1892 i c g
- Lomagostus Villiers, 1958 g
- Monteithostolus Štys, 1981 g
- Nesenicocephalus Usinger, 1939 i c g
- Oncylocotis Stål, 1855 g
- Paenicotechys Štys, 1969 g
- Paralienates Maldonado-Capriles, Santiago-Blay & Poinar, 1996 g
- Phaenicocleus Štys & Banar, 2009 g
- Phthirocoris Enderlein, 1904 g
- Phthirostenus c g
- Proboscidopirates Villiers, 1958 g
- Pyrenicocephalus Štys, 2010 g
- Stenopirates Walker, 1873 g
- Systelloderes Blanchard, 1852 i c g b
- Tornocrusus Kritsky, 1977 g
- Xenicocephalus Wygodzinsky & Schmidt, 1991
Data sources: i = ITIS,[2] c = Catalogue of Life,[3] g = GBIF,[4] b = Bugguide.net[5]
Fossil genera
- †Allocephalocoris Luo et al., 2020 Burmese amber, Myanmar, Cenomanian
- †Disphaerocephalus Cockerell 1917 Burmese amber, Myanmar, Cenomanian
- †Enicocephalinus Azar et al. 1999 Lebanese amber, Barremian
- †Paralienates Maldonado Capriles et al. 1996 Dominican amber, Miocene
- †Paenicotechys Cockerell 1917, Burmese amber, Myanmar, Cenomanian
- †Pyrenicocephalus Štys 2010 London Clay, United Kingdom, Ypresian
References
- ^ Fernandes, José Antônio Marin; Weirauch, Christiane (2015). "The Unique-Headed Bugs (Enicocephalomorpha)". True Bugs (Heteroptera) of the Neotropics. Entomology in Focus. Vol. 2. pp. 91–98. doi:10.1007/978-94-017-9861-7_4. ISBN 978-94-017-9860-0.
- ^ "Enicocephalidae Report". Integrated Taxonomic Information System. Retrieved 2018-05-01.
- ^ "Browse Enicocephalidae". Catalogue of Life. Retrieved 2018-05-01.
- ^ "Enicocephalidae". GBIF. Retrieved 2018-05-01.
- ^ "Enicocephalidae Family Information". BugGuide.net. Retrieved 2018-05-01.
