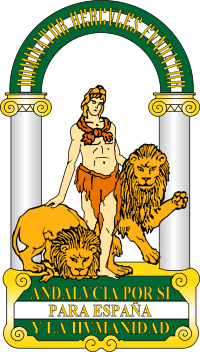
The Emblem of Andalusia (Spanish: Escudo de Andalucía) is the official symbol of Andalusia, an autonomous community of Spain. It bears the Pillars of Hercules, the ancient name given to the promontories that flank the entrance to the Strait of Gibraltar. Although often referred to as a coat of arms (or escudo in Spanish), it is technically an emblem as it was not designed to conform to traditional heraldic rules.
Origin
The emblem sees its origin in an agreement made by the pro-autonomist Assembly of Ronda in 1918, designed by Blas Infante, "Father of Andalusia".[1] More than seventy years later, article 3 of the 1982 Statute of Autonomy for Andalusia[2] stated:
Andalusia will have its own emblem, approved de jure by its Parliament, in which the following legend shall appear: "ANDALUCÍA POR SÍ, PARA ESPAÑA Y LA HUMANIDAD" (Andalusia by herself, for Spain and for Humankind), taking into account the agreement adopted by the Assembly of Ronda of 1918."[3]
The figure of the mythical Greek hero Heracles (Latin: Hercules), son of Zeus and the mortal Alcmena, appears between the columns. He is seen seizing and taming two lions, each representing the power of animal instinct, above the legend: "ANDALUCÍA POR SÍ, PARA ESPAÑA Y LA HUMANIDAD". An arc joins the two columns with the Latin inscription: "DOMINATOR HERCULES FUNDATOR". Many of these elements were adopted from the arms of the city of Cádiz.
According to Blas Infante, the creation of the emblem can in no way be seen as a meaningless invention, but as that of a series of modifications of traditional Andalusian elements: "We, Andalusian regionalists or nationalists, have not come to invent anything new. We had simply recognised, in our action, what the people created on its own, hence giving due value to its history ".
In the original coat of arms, Infante included the words "BETICA-ANDALUS", as a reminder of two of the most important periods of the history of Andalusia.
See also
References
- ^ Blas Infante is considered as the Father of the Andalusian Fatherland (Padre de la Patria Andaluza), officially recognised in Law 6/83, passed by the Andalusian Parliament on 13–14 April 1983
- ^ "LEY ORGÁNICA 6/1981, de 30 de diciembre, de Estatuto de Autonomía para Andalucía" (in Spanish). Boletín Oficial del Estado. Archived from the original on 2007-12-04. Retrieved 2008-01-06.
- ^ "Símbolos de Andalucía" (in Spanish). Junta de Andalucía. Archived from the original on 2007-10-23. Retrieved 2007-11-09.