| Gnome fruit-eating bat | |
|---|---|

| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Chiroptera |
| Family: | Phyllostomidae |
| Genus: | Dermanura |
| Species: | D. gnoma
|
| Binomial name | |
| Dermanura gnoma Handley, 1987
| |
| |
| Synonyms | |
|
Artibeus gnomus | |
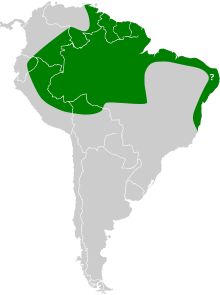
The gnome fruit-eating bat (Dermanura gnoma) is a bat species found in Bolivia, Brazil, Colombia, Ecuador, French Guiana, Guyana, Peru, Suriname and Venezuela. This species was originally determined to be different from the other known species of fruit bats, but later, in 1994 was mistakenly grouped under Artibeus cinereus as a synonym.[2] However, this has since been corrected by more closely studying their physical differences and by biomolecular analysis.[3][4][5]
YouTube Encyclopedic
-
1/5Views:4 665 7882 545 9335 862 4397 254 548933 308
-
Adam Eats An Entire Mushroom Chocolate Bar | Vital Educational Content
-
61 Year Old Tries "Magic Mushrooms" (psilocybin) | DOCUMENTARY
-
Unusual Kids Born with Super Unique Conditions
-
Things You Do Wrong Every Day
-
Unboxing Praying Mantises Bred by a 9-Year-Old!
Transcription
References
- ^ Solari, S. (2015). "Dermanura gnoma". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2015. e.T2129A97207684. doi.org/10.2305/IUCN.UK.2015-4.RLTS.T2129A21997242.en. Downloaded on 18 February 2020.
- ^ Koopman, K.F. (1994). Chiroptera: systematics. Handbook of zoology: a natural history of the phyla of the animal kingdom VIII. New York, USA: Walter de Gruyter.
- ^ Solari, S.; Hoofer, SR.; Larsen, P.A.; Brown, A.D.; Bull, R.J.; Guerrero, J.A.; Ortega, J.; Carrera, J.P.; Bradley, R.D. & Baker, R.J. (2009). "Operational Criteria for Genetically Defined Species: Analysis of the Diversification of the Small Fruit-Eating Bats, Dermanura (Phyllostomidae: Stenodermatinae)". Acta Chiropterologica. 11 (2): 279–288. doi:10.3161/150811009X485521. S2CID 15355333.
- ^ Simmons, N.B. (2005). Mammal Species of the World. Baltimore, MD, USA.: The Johns Hopkins University Press. pp. 312–529.
- ^ Hoofer, S.R.; Solari, S.; Larsen, P.A.; Bradley, R.D. & Baker, R.J. (2008). "Phylogenetics of the fruit-eating bats (Phyllostomidae: Artibeina) inferred from mitochondrial DNA sequences". Occasional Papers, Museum of Texas Tech University. 272: 1–15.
External links

