| Hesperocyparis sargentii | |
|---|---|

| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Gymnospermae |
| Division: | Pinophyta |
| Class: | Pinopsida |
| Order: | Cupressales |
| Family: | Cupressaceae |
| Genus: | Hesperocyparis |
| Species: | H. sargentii
|
| Binomial name | |
| Hesperocyparis sargentii (Jeps.) Bartel (2009)
| |
| |

| |
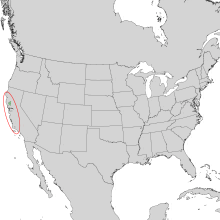
| Natural range | |
| Synonyms[3] | |
| |
Hesperocyparis sargentii is a species of conifer in the family Cupressaceae known by the common name Sargent's cypress. It is endemic to California, where it is known from Mendocino County southwards to Santa Barbara County. This taxon is limited to the Coast Range mountains. It grows in forests with other conifers, as well as chaparral and other local mountain habitat, usually in pure stands on serpentine soils. It generally grows 10 to 15 meters (33–50 feet) tall, but it is known to exceed 22 meters (73 feet). On Carson Ridge in Marin County, as well as Hood Mountain in Sonoma County, the species comprises a pygmy forest of trees which do not attain heights greater than 240–360 cm (8–12 feet) due to high mineral concentrations in the serpentine soil.[4]
One notable population occurs in the Cedar Mountain Ridge area of Eastern Alameda County. According to Carl Wolf, who extensively studied the New World Cypress in the 1930s and 1940s, seed from the Cedar Mountain stand of Cupressus sargentii produced the most vigorous seedlings.
Like many of the New World Cupressaceae, Sargent cypress usually reproduces with the aid of wildfire, which cause an opening of the cones and exposure of bare mineral soil for seedling germination, though occasionally seeds will fall and germinate without fire, though such seems to be the exception rather than the rule. It is often the case that many trees in a particular stand will all be the same age, so that a sort of stratification occurs of different colonies all of the same age. Sargent cypress can begin producing cones as early as five or six years of age.[5]
Taxonomy
Hesperocyparis sargentii was scientifically described by the botanist Willis Linn Jepson in 1909 and given the name Cupressus sargentii.[3] He found the type specimen in the Mayacamas Mountains in northern California.[6] Jepson also identified a variety of the species, var. duttonii, in 1923, but this has not become widely accepted.[3] For almost 100 year the status of the species was not disturbed until in 2006 the first of several proposals to move it to, Callitropsis alongside Callitropsis nootkatensis. Further research lead to two proposals to move it to a new genus for new world species of cypress, Neocupressus and Hesperocyparis.[3] As of 2024[update] Hesperocyparis sargentii is considered to be the correct classification by Plants of the World Online,[3] World Flora Online,[7] and the USDA Natural Resources Conservation Service PLANTS database.[8]
References
- ^ Farjon, A. (2013). "Cupressus sargentii". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2013: e.T42258A2967745. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2013-1.RLTS.T42258A2967745.en. Retrieved 15 November 2021.
- ^ NatureServe (2024). "Cupressus sargentii". Arlington, Virginia. Retrieved 15 February 2024.
- ^ a b c d e "Hesperocyparis sargentii (Jeps.) Bartel". Plants of the World Online. Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew. Retrieved 15 February 2024.
- ^ Biohere, Hood Mountain Park
- ^ Wolf, C. B. & Wagener, W. E. (1948). The New World cypresses. El Aliso 1: 195-205.
- ^ Jepson, Willis Linn (1909). A Flora of California. San Francisco, California: Cunningham, Curtis & Welch. p. 61. Retrieved 16 February 2024.
- ^ "Hesperocyparis sargentii (Jeps.) Bartel". World Flora Online. Retrieved 16 February 2024.
- ^ Hesperocyparis sargentii, USDA Natural Resources Conservation Service PLANTS Profile, 16 February 2024
Further reading
- Forest Service Fire Ecology
- Wolf, C. B. & Wagener, W. E. (1948). The New World cypresses. El Aliso 1: 195–205.
External links
- Jepson Manual Treatment of Cupressus sargentii
- USDA Plants Profile for Cupressus sargentii
- Flora of North America
- UC CalPhotos gallery


