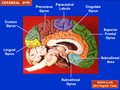
| Cuneus | |
|---|---|
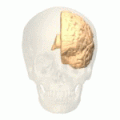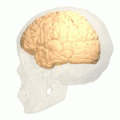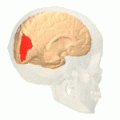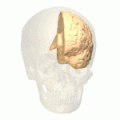
 Medial surface of left cerebral hemisphere. (Cuneus visible at left in red.) | |
 Sagittal MRI slice with the cuneus and lingual gyrus shown in red. | |
| Details | |
| Artery | posterior cerebral artery |
| Identifiers | |
| NeuroNames | 157 |
| NeuroLex ID | birnlex_1396 |
| TA98 | A14.1.09.224 |
| TA2 | 5485 |
| FMA | 61903 |
| Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy | |
The cuneus (from Latin 'wedge'; pl.: cunei) is a smaller lobe in the occipital lobe of the brain. The cuneus is bounded anteriorly by the parieto-occipital sulcus and inferiorly by the calcarine sulcus.
YouTube Encyclopedic
-
1/5Views:1 7301 87510 44644 156700 310
-
Parieto-occipital & calcarine sulci, cuneus & lingual gyri, and pre-Cuneus
-
How To Say Cuneus
-
Frontal Lobe | Cerebral Cortex
-
The Neurobiology of Prefrontal Cortex and its Role in Mental Disorders
-
Virtual Rome: What did the Colosseum look like?
Transcription
Function
The cuneus (Brodmann area 17) receives visual information from the same-sided superior quadrantic retina (corresponding to contralateral inferior visual field). It is most known for its involvement in basic visual processing. Pyramidal cells in the visual cortex (or striate cortex) of the cuneus, project to extrastriate cortices (BA 18,19). The mid-level visual processing that occurs in the extrastriate projection fields of the cuneus are modulated by extraretinal effects, like attention, working memory, and reward expectation.
Clinical research
In addition to its traditional role as a site for basic visual processing, gray matter volume in the cuneus is associated with better inhibitory control in bipolar depression patients.[1]
Pathologic gamblers have higher activity in the dorsal visual processing stream including the cuneus relative to controls.[2]
Gallery
-
Position of cuneus(red) of left cerebral hemisphere.
-
Medial surface of left cerebral hemisphere. Cuneus is visible at left in green.
-
Infero-medial surface of right cerebral hemisphere. The color brown represents occipital lobe.
-
Medial surface of right cerebral hemisphere. Cuneus labeled at right.
-
Cuneus, shown in the right cerebral hemisphere.
-
Cuneus highlighted in green on coronal T1 MRI images
-
Cuneus highlighted in green on sagittal T1 MRI images
-
Cuneus highlighted in green on transversal T1 MRI images
References
- ^ Haldane M, Cunningham G, Androutsos C, Frangou S (March 2008). "Structural brain correlates of response inhibition in Bipolar Disorder I". Journal of Psychopharmacology. 22 (2): 138–43. doi:10.1177/0269881107082955. PMID 18308812.
- ^ Crockford DN, Goodyear B, Edwards J, Quickfall J, el-Guebaly N (November 2005). "Cue-induced brain activity in pathological gamblers" (PDF). Biological Psychiatry. 58 (10): 787–95. doi:10.1016/j.biopsych.2005.04.037. PMID 15993856.
- Sherrington, Charles Scott (1911). . In Chisholm, Hugh (ed.). Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. 4 (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press. pp. 391–413. See p. 397 for reference to "cuneus".