| Cortical reaction | |
|---|---|
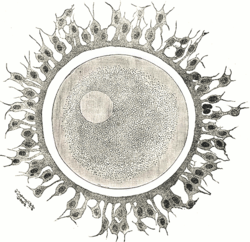 Human ovum. The zona pellucida is seen as a thick clear girdle surrounded by the cells of the Corona radiata. | |
| Anatomical terminology |
The cortical reaction is a process initiated during fertilization that prevents polyspermy, the fusion of multiple sperm with one egg. In contrast to the fast block of polyspermy which immediately but temporarily blocks additional sperm from fertilizing the egg, the cortical reaction gradually establishes a permanent barrier to sperm entry and functions as the main part of the slow block of polyspermy in many animals.
To create this barrier, cortical granules, specialized secretory vesicles located within the egg's cortex (the region directly below the plasma membrane), are fused with the egg's plasma membrane. This releases the contents of the cortical granules outside the cell, where they modify an existing extracellular matrix to make it impenetrable to sperm entry. The cortical granules contain proteases that clip perivitelline tether proteins, peroxidases that harden the vitelline envelope, and glycosaminoglycans that attract water into the perivitelline space, causing it to expand and form the hyaline layer. The trigger for the cortical granules to exocytose is the release of calcium ions from cortical smooth endoplasmic reticulum in response to sperm binding to the egg.
In most animals, the extracellular matrix present around the egg is the vitelline envelope which becomes the fertilization membrane following the cortical reaction. In mammals, however, the extracellular matrix modified by the cortical reaction is the zona pellucida. This modification of the zona pellucida is known as the zona reaction. Although highly conserved across the animal kingdom, the cortical reaction shows great diversity between species. While much has been learned about the identity and function of the contents of the cortical granules in the highly accessible sea urchin, little is known about the contents of cortical granules in mammals.
The cortical reaction within the egg is analogous to the acrosomal reaction within the sperm, where the acrosome, a specialized secretory vesicle that is homologous to cortical granules, is fused with the plasma membrane of the sperm cell to release its contents which degrade the egg's tough coating and allow the sperm to bind to and fuse with the egg.
YouTube Encyclopedic
-
1/3Views:220 30935 079251 863
-
General Embryology - Detailed Animation On Fertilization
-
Developmental biology part 4 : sea urchin fertilization
-
Egg, sperm, and fertilization | Behavior | MCAT | Khan Academy
Transcription
when ejaculation occurs during intercourse approximately 200 million sperm or spermatozoa are deposited into the vagina they swim through the cervix propelled by with whip-like motions of their tails or Flagela after which muscular contractions of the uterus direct them to the uterine tubes this process usually takes between 30 minutes and two hours only around 200 spermatozoa will reach the secondary oocyte in the uterine tube and of these only one will fertilize it fertilization cannot occur until two processes have taken place capacitation and the acrosomal reaction these can take several hours capacitation is not fully understood but secretions from the uterus wall and uterine tube destabilize the plasma membrane surrounding the head the spermatozoa or acrosome resulting in the membrane becoming more fluid which helps to prepare the spermatozoa for the events a fertilization the spermatozoa become hyperactive their flagella beat more frequently and their heads move laterally the capacitated spermatozoa moved through the corona radiata a dense layer of granulosa cells surrounding the oocyte and come into contact with the zona pellucida the zona pellucida expresses specific receptor proteins called ZP3 which bind to proteins expressed in the heads of the spermatozoa the binding ZP3 triggers the acrosome reaction during which the enzymatic contents of the acrosome are released these enzymes help to digest a path through the zona pellucida allowing the spermatozoa to enter the perivitelline space and reach the plasma membrane of the secondary oocyte with which it fuses to ensure that only one spermatozoa and penetrates the zona pellucida infuses with the oocyte membrane fusion of the spermatozoon and oocyte membranes activates a fast and a slow block to polyspermy during fast blocked polyspermy after fusion the oocyte membrane depolarizes preventing other spermatozoa from fusing with it slow block to polyspermy is also stimulated by this depolarization during slow block to polyspermy a wave of intracellular calcium is released causing small cortical granules beneath the oocyte membrane to release their contents renderings ZP3 inactive and making the zona pellucida impermeable upon the spermatozoon entering the oocyte undergoes meiosis II and further develops into the female pro nucleus during this time the sperm develops into the male pro nucleus and the two Pro nuclei fuse to form a single diploid nucleus or zygote
Echinoderms
In the well-studied sea urchin model system, the granule contents modify a protein coat on the outside of the plasma membrane (the vitelline layer) so that it is released from the membrane. The released cortical granule proteins exert a colloid osmotic pressure causing water to enter the space between the plasma membrane and the vitelline layer, and the vitelline layer expands away from the egg surface. This is easily visible through a microscope and is known as "elevation of the fertilization envelope". Some of the former granule contents adhere to the fertilization envelope, and it is extensively modified and cross-linked. As the fertilization envelope elevates, non-fertilizing sperm are lifted away from the egg plasma membrane, and as they are not able to pass through the fertilization envelope, they are prevented from entering the egg. Therefore, the cortical reaction prevents polyspermic fertilization, a lethal event. Another cortical granule component, polysaccharide-rich hyalin, remains adherent to the outer surface of the plasma membrane, and becomes part of the hyaline layer.
Mammals
Although various mammals have been studied, mice represent the best studied animal models for understanding the cortical reaction in mammals. In mammals the cortical reaction leads to a modification of the zona pellucida that blocks polyspermy; enzymes released by cortical granules digest sperm receptor glycoproteins ZP2 and ZP3 so that they can no longer bind spermatozoon.
See also
- Acrosome reaction - The analogous reaction in the acrosome of the sperm
References
- Haley SA, Wessel GM. Sea urchin cortical granules regulated proteolysis by cortical granule serine protease 1 at fertilisation. Mol Biol Cell. 2004 May;15(5):2084-92.
- Sadler TW. Langman's Medical Embryology. Baltimore: Lippincott Williams and Wilkins, 2006.
