| Tesseract 16-cell compound | |
|---|---|
| Type | Compound |
| Schläfli symbol | {4,3,3} ∪ {3,3,4} |
| Coxeter diagram | |
| Intersection | bitruncated tesseract |
| Convex hull | 24-cell |
| Polychora | 2: 1 tesseract 1 16-cell |
| Polyhedra | 24: 8 cubes 16 tetrahedra |
| Faces | 56: 24 squares 32 triangles |
| Edges | 56 |
| Vertices | 24 |
| Symmetry group | Hyperoctahedral symmetry [4,3,3], order 384 |
In 4-dimensional geometry, the tesseract 16-cell compound[1] is a polytope compound composed of a regular tesseract and its dual, the regular 16-cell. Its convex hull is the regular 24-cell, which is self-dual.
A compound polytope is a figure that is composed of several polytopes sharing a common center. The outer vertices of a compound can be connected to form a convex polytope called its convex hull. The compound is a facetting of the convex hull. In 4-polytope compounds constructed as dual pairs, cells and vertices swap positions and faces and edges swap positions. Because of this the number of cells and vertices are equal, as are faces and edges. Mid-edges of the tesseract cross mid-face in the 16-cell, and vice versa.
The tesseract 16-cell compound can be seen as the 4-dimensional analogue of a compound of cube and octahedron.
It is one of four compound polytopes which are obtained by combining a regular convex 4-polytope with its dual; the other three being the compound of two 5-cells, compound of two 24-cells and compound of 120-cell and 600-cell.
Construction
The 24 Cartesian coordinates of the vertices of the compound are:
- 8: (±2, 0, 0, 0), ( 0, ±2, 0, 0), ( 0, 0, ±2, 0), ( 0, 0, 0, ±2)
- 16: ( ±1, ±1, ±1, ±1)
These are the first two vertex sets of the stellations of a 16-cell.[2]
Faceting the 24-cell
The convex hull of the tesseract 16-cell compound is the regular 24-cell. This makes the compound a faceting of the 24-cell.
The 24-cell is a rectified 16-cell and also the convex hull of a compound of three 16-cells. The tesseract is the convex hull of a compound of two 16-cells. Thus the tesseract 16-cell compound is a lower-symmetry form of the 24-cell, which is the whole package (the F4 symmetry group).
The intersection of the tesseract and 16-cell compound is the uniform bitruncated tesseract: ![]()
![]()
![]() =
= ![]()
![]()
![]() ∩
∩ ![]()
![]()
![]() .
.
| Elements | Compound | Convex hull | Intersection | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
 Tesseract |
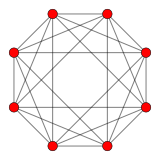 16-cell |
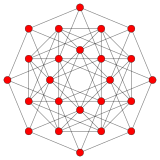 Tesseract and 16-cell |
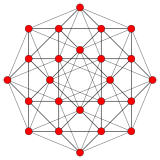 24-cell |
 Bitruncated tesseract |
See also
References
- ^ Klitzing, Richard. "Compound polytopes".
- ^ The Stellated Forms of the Sixteen-Cell B. L. Chilton The American Mathematical Monthly Vol. 74, No. 4 (Apr., 1967), pp. 372–378
