
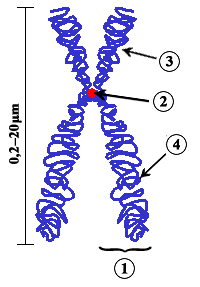
Several chromosome regions have been defined by convenience and convention in order to talk about gene loci. The largest regions on each chromosome are the short arm p and the long arm q, separated by a narrow region near the center called the centromere.[1] Other specific regions have also been defined, some of which are similarly found on every chromosome, while others are only present in certain chromosomes.
Named regions include:
- Arms (p and q)
- Centromere
- Kinetochore
- Telomere
- Sub telomere
- satellite chromosome or trabant.
- NOR region
During cell division, the molecules that compose chromosomes (DNA and proteins) undergo a condensation process (called the chromatin reticulum condensation) that forms a compact and small complex called a chromatid. The complexes containing the duplicated DNA molecules, the sister chromatids,[2] are attached to each other by the centromere(where the Kinetochore assembles).
If the chromosome is a submetacentric chromosome (One arm big and the other arm small) then the centromere divides each chromosome into two regions: the smaller one, which is the p region, and the bigger one, the q region. The sister chromatids will be distributed to each daughter cell at the end of the cell division. Whereas if the chromosome is isobrachial (centromere at centre and arms of equal length), the p and q system is meaningless.
At either end of a chromosome is a telomere, a cap of DNA that protects the rest of the chromosome from damage. The telomere has repetitive junk DNA and hence any enzymatic damage will not affect the coded regions. The areas of the p and q regions close to the telomeres are the subtelomeres, or subtelomeric regions. The areas closer to the centromere are the pericentronomic regions. Finally, the interstitial regions are the parts of the p and q regions that are close to neither the centromere nor the telomeres, but are roughly in the middle of p or q.

YouTube Encyclopedic
-
1/3Views:8 5171 1932 010
-
Cytogenetics II Chromosome Translocations
-
5 Questions You Can Answer With NCBI Nucleotide
-
Selection in Action
Transcription
See also
References
- ^ National Center for Biotechnology Information (US) (1998). "Chromosome Map". Genes and Disease [Internet]. National Center for Biotechnology Information (US). Retrieved 24 November 2023.
- ^ "National Human Genome Research Institute (NHGRI) - Centromere". National Human Genome Research Institute (NHGRI). Retrieved 2018-11-19.
