Commonwealth of Independent States Free Trade Area | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Type | Free-trade area |
| Member states | |
| Establishment | |
• Free trade agreement signed | 18 October 2011 |
• Free Trade Area established | 20 September 2012 |
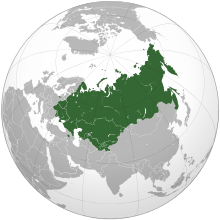
Commonwealth of Independent States Free Trade Area (CISFTA) is a free-trade area among Russia, Ukraine, Belarus, Uzbekistan, Moldova, Armenia, Kyrgyzstan, Kazakhstan and Tajikistan. Five CISFTA participants, all except Ukraine, Uzbekistan, Moldova and Tajikistan, are members of the Eurasian Economic Union, comprising a single economic market, although Uzbekistan and Moldova are observers.
YouTube Encyclopedic
-
1/5Views:859672 1902 098 36437811 708 191
-
Commonwealth of Independent States
-
(Almost) Every Multinational Union Explained
-
How are the former Soviet countries doing today?
-
Refining Sugar, Capitalism and Corporate PR in the British Commonwealth in the 1940s and 1950s
-
The European Union Explained*
Transcription
History
The Commonwealth of Independent States Free Trade Zone Agreement, proposed since the breakup of the Soviet Union in 1991, was signed on 18 October 2011 by Russia, Ukraine, Belarus, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Moldova and Armenia.[citation needed] The agreement replaces existing bilateral and multilateral free trade agreements among the countries. Initially, the treaty was only ratified by Russia, Belarus, and Ukraine,[1][2] however by the end of 2012, Kazakhstan, Armenia, and Moldova had also completed ratification.[3][4] In December 2013, Uzbekistan signed and then ratified the treaty,[5][6] while the remaining two signatories, Kyrgyzstan and Tajikistan, later both ratified the treaty in January 2014 and December 2015 respectively.[7][8] Azerbaijan is the only full CIS member state not to participate in the free trade area.
European Union–Ukraine trade agreement controversy
From 1 January 2016, Ukraine and the European Union started provisionally applying a Deep and Comprehensive Free Trade Agreement. Member states of the Eurasian Economic Union (EEU or EAEU) held consultations on 22 December 2015 to discuss the implications of the agreement concerning the possible duty-free transit of EU goods into the EEU via Ukraine. The states agreed to implement a provisional scheme later in 2016 that would impose customs checks on goods entering the EEU from Ukraine; and long term, to establish a common information system to control all imports into the EEU's customs area.[9] Nonetheless, Russia promulgated a decree in mid-December 2015 suspending its CIS Free Trade Agreement with respect to Ukraine from 1 January 2016.[10] In late December, the Ukrainian Government responded by passing trade restrictions on Russia, with effect from 2 January 2016.[11] Agreements between Ukraine and other EEU states within the free trade area remain in effect.
On 1 November 2022, Verkhovna Rada MP Roksolana Pidlasa made a draft bill to denounce the proposed to Treaty on the Free Trade Area (CIS) dated 18 October 2011. After meeting with Prime Minister Denys Shmyhal, she said, "It is time to decolonize our trade. We have bilateral free trade agreements with all CIS member countries, the GUAM Free Trade Agreement, and we also apply the Pan-Euro-Med regional convention with Georgia and Moldova. There are many tools that work for Ukrainian manufacturers. There is no need to participate in a treaty where Russia imposes its rules and uses the right of force."[12]
Signature and ratification

An overview of signatures and ratifications is shown below:
| State | Signature | Entry into Force[13] | Comment |
|---|---|---|---|
| 18 October 2011 | 17 October 2012 | EAEU member | |
| 18 October 2011 | 20 September 2012 | EAEU member | |
| 18 October 2011 | 8 December 2012 | EAEU member | |
| 18 October 2011 | 13 December 2013 | EAEU member | |
| 18 October 2011 | 9 December 2012 | EAEU observer | |
| 18 October 2011 | 20 September 2012 | EAEU member | |
| 18 October 2011 | 19 March 2016 | ||
| 18 October 2011 | 20 September 2012 | Former CIS participant | |
| 13 December 2013 | 12 January 2014 | EAEU observer |
In 2013, the protocol on the application of the CIS FTA between Uzbekistan and the CIS FTA member states was signed as a bilateral document and without any reservations to the CIS FTA agreement.[15] It entered into force in 2014.[16]
See also
- Commonwealth of Independent States
- Economic integration
- Eurasian Union
- Free trade areas in Europe
- Post-Soviet states
- Trade bloc
- Rules of Origin
- Market access
- Free-trade area
- Tariff
References
Footnotes
Online sources
- ^ Russia’s Duma ratifies Eurasian Economic Union Archived 22 June 2018 at the Wayback Machine, odessatalk.com. Retrieved 23 December 2014.
- ^ CIS Free Trade Agreement comes into force; Baker & McKenzi, Kyiv, Ukraine, Thursday, October 18, 2012, 18 October 2011
- ^ Kazakhstan ratified agreement on Free Trade zone Archived 22 June 2018 at the Wayback Machine www.kaztag.kz. Retrieved 22 June 2018.
- ^ Armenia ratifies CIS free trade zone agreement, arka.am. Retrieved 22 June 2018.
- ^ Usbekistan: Protokoll über Beitritt zur GUS-Freihandelszone in Kraft getreten, de.ria.ru 28 December 2013.
- ^ Uzbekistan joins CIS free trade zone, azernews.az. Retrieved 23 December 2014.
- ^ Dushanbe ratifies agreement on CIS free trade area Archived 22 June 2018 at the Wayback Machine, Vestnik Kavkaza. Retrieved 22 June 2018.
- ^ Tajikistan ratifies CIS Free Trade Zone Agreement, AKIpress. Retrieved 22 June 2018
- ^ Belarus, Russia, Kazakhstan work out provisional scheme to control transit via Ukraine, Belarus News. Retrieved 4 January 2016.
- ^ "Russia suspends FTA with Ukraine as EU agreement looms". Eurasian Business Briefing. 17 December 2015. Archived from the original on 25 December 2015. Retrieved 24 December 2015.
- ^ Spotlight: EU-Ukraine trade deal triggers new round of economic clashes, news.xinhuanet.com. Retrieved 4 January 2016.
- ^ "Україна денонсує договір про вільну торгівлю з СНД". www.ukrinform.ua (in Ukrainian). Retrieved 1 February 2023.
- ^ "Идет перенаправление".
- ^ "Eurasian Economic Union: The rocky road to integration - Think Tank". www.europarl.europa.eu. Retrieved 9 February 2019.
- ^ "Главы правительств стран СНГ подписали протокол о присоединении Узбекистана к договору о зоне свободной торговли | Экономика". Archived from the original on 8 January 2014.
- ^ https://cis.minsk.by/reestrv2/doc/3868
