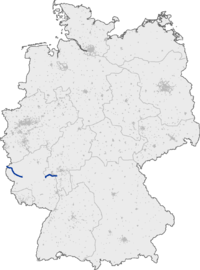
Bundesautobahn 60 (translates from German as Federal Motorway 60, short form Autobahn 60, abbreviated as BAB 60 or A 60) is an autobahn in Germany. During its entire course it forms a part of the E 42.
YouTube Encyclopedic
-
1/1Views:3 233
-
Autobahn A60 Bingen - Mainz, Germany
Transcription
Overview
The A 60 begins at the former border crossing Steinebrück four lanes as a continuation of the Belgian A 27 from Liège. The state border runs on the 411 meter long Ourtalbrücke, which crosses the border between Belgium and Germany. This section of the route to Wittlich is also called the Eifel motorway. On the German side is behind the valley bridge a parking lot, which was originally created as a customs facility. A similar institution exists on the Belgian side on the other side of the Our. Directly behind the first connection point Winterspelt (2), only the northern directional carriageway is completed, over which the traffic is ever guided. The complete expansion of the section is listed in the Federal Transport Infrastructure Plan as "Further Demand". However, an expansion is not foreseeable due to the very low traffic volume throughout the route section. Thus, some smaller bridges and all overpass structures have already been built for four lanes, the three large bridges but only completed for two lanes. In some places, however, a third lane was marked to allow overtaking. Furthermore, the section is provided with yellow kilometer for federal roads.
The following section between Prüm (4) and Bitburg (6) was for a long time also only two-lane developed. However, many serious accidents resulted in priority being given to the expansion. Due to the many viaducts, the expansion was only completed in 2000 with the completion of the Nimstal bridge. Between Bitburg (6) and Badem (7), the route passes through the Kylltalbrücke near Wilsecker, which, with a span of 223 m, is one of the largest reinforced concrete arch bridges in Germany.
The first section of the A 60 ends at the interchange Wittlich, where the A 1 (Fehmarn-Hamburg-Bremen-Cologne-Saarbrücken) is crossed. The gap closure to Bingen is as B 50 new (Hochmoselübergang) built. Between the cross Wittlich and plates the route is since 15 December 2014 four lanes under traffic, the subsequent section to Longkamp with the 158 m high Hochmoselbrücke, a tunnel and three other large bridges is under construction.The federal highway is then to be expanded to Hahn airport four lanes and there on the completed since 2011 section in Rheinböllen in the A 61, over which the second section of the A 60 can be achieved. With the completion of the motorway, it will be the shortest link between the Rhine-Main area and Luxembourg or Wallonia. The gap closure should however also have positive effects on the economy and the tourism in the entire Eifel Mosel region, since then it is well connected in all directions.
The second section of the A 60 starts at the motorway junction Nahetal on the A 61 between Bingen am Rhein and Gensingen. This is like a motorway junction expanded and thus still testifies to the planned gap closure as a continuous highway to Wittlich. The route leads four lanes immediately south of the Rhine past Ingelheim and Heidesheim am Rhein to the motorway junction Mainz, where the A 643 branches off to Wiesbaden. From the Ingelheim-West interchange, the hard shoulder of the southern, from the junction Heidesheim also the hard shoulder of the northern directional lane in each case up to the triangle Mainz to a regular third lane is marked and instead, isolated emergency shelters have been built. Subsequently, the A 60 forms the southern part of the Mainz ring and leads south around Mainz. Up to the intersection Mainz-South, it is only four-lane without hard shoulder and equipped with emergency shelters. At the intersection Mainz-Süd begins the A 63 direction Kaiserslautern. From the Mainz-South intersection to the Ginsheim-Gustavsburg interchange, the motorway was expanded to six lanes starting in the late 1990s, with the side lanes being rebuilt on the Rhine bridge. For reasons of noise protection, the motorway was lowered and a noise protection tunnel was built at Mainz-Hechtsheim. Since the official release on 10 August 2012 there are three lanes in each direction and the exit Mainz-Hechtsheim-Ost is now in the tunnel. In the Hechtsheim area, there are no more highway bridges, the highway runs under the road and the local tram. A full expansion to six lanes with hard shoulder also between Ingelheim-West and Cross Mainz-South is included in the urgent need - bottleneck elimination of the Federal Transport Infrastructure Plan 2030. For the section between Dreieck Mainz and Kreuz Mainz-Süd, including reconstruction of the Mainz-Süd cross, the design planning was carried out at the end of 2016. A six-lane expansion between Dreieck Nahetal and Ingelheim-West is also included in the Federal Transport Infrastructure Plan, but only in the category Additional Demand with Planning Law.
After crossing the Rhine on the Weisenauer bridge you are in Hesse. Immediately after that, the Mainspitz-Dreieck connects the A 671 to Wiesbaden and Mainz-Kastel, which forms the eastern part of the Mainzer Ring. At Bischofsheim and south past Rüsselsheim am Main, the A 60 at the Rüsselsheim Triangle joins the A 67 (Frankfurt-Darmstadt-Mannheim). The section east of the Mainspitz triangle is currently only four-lane with hard shoulder expanded, but should also be expanded six-lane (Priority needs - bottleneck removal of the Federal Transport Infrastructure Plan).[1]
Exit list
| Belgium | ||
| Ourtalbrücke 710 m (Belgium) | ||
| (1) | Border crossing Steinbrück | |
| parking area | ||
| (2) | Winterspelt | |
| Talbrücke Ihren 130 m | ||
| (3) | Bleialf | |
| Alfbachtalbrücke 330 m | ||
| Schneifel parking area | ||
| Mönbachtalbrücke 440 m | ||
| Prümtalbrücke 710 m | ||
| (4) | Prüm | |
| Talbrücke Heisdorf 280 m | ||
| Prümer Land parking area | ||
| (5) | Waxweiler | |
| Rest area Nimstal | ||
| Rest area Nimstal (planned) | ||
| Nimstalbrücke 781 m | ||
| (6) | Bitburg | |
| Kylltalbrücke 645 m | ||
| (7) | Badem | |
| Wolfskaulbrücke 162 m | ||
| Gindorf parking area | ||
| Weilbachtalbrücke 60 m | ||
| Talbrücke Spangerbach 272 m | ||
| (8) | Spangdahlem | |
| Talbrücke Kailbach 340 m | ||
| (9) | Landscheid | |
| Salmtalbrücke 653 m | ||
| Bergweiler (planned) | ||
| Talbrücke Bergweiler 430 m | ||
| Rest area Fintenkapelle | ||
| (10) | Wittich-West | |
| Talbrücke Königsbuche 178 m | ||
| (11) | Wittlich 4-way interchange | |
|
| ||
| (12) | Nahetal 3-way interchange | |
| (13) | Bingen-Ost | |
| Rüdesheim (planned) | ||
| (15) | Ingelheim-West | |
| (16) | Ingelheim-Ost | |
| Services Heidenfahrt | ||
| Heidenfahrt parking area | ||
| (17) | Heidesheim | |
| (18) | Mainz 3-way interchange | |
| Gonsbachbrücke 200 m | ||
| (19) | Mainz-Finthen | |
| (20) | Mainz-Lerchenberg | |
| (21) | Mainz-Süd 4-way interchange | |
| (22a) | Mainz-Hechtsheim-West (Messe) | |
| Tunnel Mainzer Autobahntunnel | ||
| (22b) | Mainz-Hechtsheim-Ost | |
| (23) | Mainz-Weisenau | |
| (24) | Mainz-Laubenheim | |
| Weisenauer Brücke 900 m | ||
| (25) | Ginsheim-Gustavsburg | |
| (26) | Mainspitz-Dreieck 3-way interchange | |
| (27) | Bischofsheim | |
| (28) | Rüsselsheim-Mitte | |
| (29) | Rüsselsheim-Königstädten | |
| (30) | Rüsselsheim 3-way interchange | |
References
External links
- Bundesautobahn 60 – detailed route plan (in German)
49°58′40″N 8°27′50″E / 49.97778°N 8.46389°E