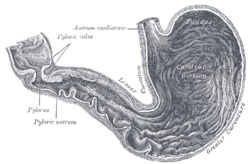
The duodenal bulb (also ampulla of duodenum, duodenal ampulla, or duodenal cap) is the initial, dilated portion of (the superior part of) the duodenum[1] just distal to the stomach; it begins at the pylorus and ends at the neck of the gallbladder. It is normally about 5 centimeters long.[2]
YouTube Encyclopedic
-
1/3Views:3 85072 8311 107
-
Analysis of Biopsies From Duodenal Bulbs of All Endoscopy Patients...
-
Peptic Ulcer Disease: GASTRIC VS DUODENAL ULCERS
-
TRANSPARENT CAP FOR TREATMENT OF A BLEEDING DUODENAL ULCER
Transcription
Structure
Relations
It is located posterior to the liver and the gallbladder and superior to the pancreatic head.[citation needed] The gastroduodenal artery,[3] portal vein, and common bile duct are situated posterior to the duodenal bulb. The distal part of the bulb is located retroperitoneally. It is located immediately distal to the pyloric sphincter.[citation needed]
Clinical significance
The duodenal bulb is the site of duodenal ulcer occurrence. Duodenal ulcers are more common than gastric ulcers and - unlike gastric ulcers - are caused by increased gastric acid secretion. Duodenal ulcers are commonly located anteriorly, and rarely posteriorly. Anterior ulcers can be complicated by perforation, while the posterior ones bleed. The reason for that is explained by their location. The peritoneal or abdominal cavity is located anterior to the duodenum. Therefore, if the ulcer grows deep enough, it will perforate, whereas if a posterior ulcer grows deep enough, it will penetrate the gastroduodenal artery and bleed.[citation needed]
Notes
- ^ a b c "duodenal ampulla". TheFreeDictionary.com. Retrieved 2023-11-10.
- ^ "Normal Findings in Endoscopy: Bulbus Duodeni". GASTROLAB. Archived from the original on 2006-04-28. Retrieved 2006-04-15.
- ^ "ampoule duodénale - Dictionnaire médical de l'Académie de Médecine". www.academie-medecine.fr. Retrieved 2023-11-10.
External links
- Diagram - look for figure #2, item #5
- MedEd at Loyola Radio/curriculum/GI/sandy44a.jpg
- Images at gastrolab.net