| Aviatyrannis Temporal range: Late Jurassic,
| |
|---|---|
| |
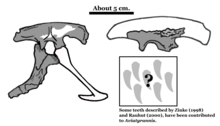
| Diagram of fossils assigned to Aviatyrannis | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Clade: | Dinosauria |
| Clade: | Saurischia |
| Clade: | Theropoda |
| Clade: | Tyrannoraptora |
| Superfamily: | †Tyrannosauroidea |
| Clade: | †Pantyrannosauria |
| Genus: | †Aviatyrannis Rauhut, 2003 |
| Species: | †A. jurassica
|
| Binomial name | |
| †Aviatyrannis jurassica Rauhut, 2003
| |
Aviatyrannis is a genus of coelurosaurian theropod dinosaur, possibly a tyrannosauroid, from the Oxfordian-Tithonian stages of the Late Jurassic found in Portugal.
Discovery and naming
In 2000 Oliver Walter Mischa Rauhut reported the find of tyrannosauroid material in the lignite coal mine of Guimarota near Leiria, which he referred to Stokesosaurus.[1] Later concluding the distinctiveness of the material justified a separate genus, Rauhut in 2003 named and described it as the type species Aviatyrannis jurassica.[2] The species name was by Rauhut given the intended meaning of "tyrant's grandmother from the Jurassic".[2] The generic name is derived from Latin avia, "grandmother", and tyrannus, "tyrant", on the presumption tyrannis would be its genitive.[2] The specific name means "Jurassic".[2]
The holotype, IPFUB Gui Th 1, was found in a layer of the Alcobaça Formation dating from the early Kimmeridgian, about 155 million years old. It consists of a right ilium. Rauhut in 2003 referred two other bones to Aviatyrannis: IPFUB Gui Th 2, a partial right ilium, and IPFUB Gui Th 3, a right ischium. The referred elements represent slightly larger individuals. Additionally sixteen isolated teeth were referred: IPFUB GUI D 89-91: three teeth of the premaxilla, and IPFUB GUI D 174-186: thirteen teeth of the maxilla and dentary.[2] These had in 1998 been described by Jens Zinke.[3] Rauhut also hypothesised that a number of specimens referred to Stokesosaurus might actually belong to Aviatyrannis.[2]
Description

Aviatyrannis was a rather small theropod. The holotype specimen IPFUB Gui Th 1, for example, is an ilium only ninety millimeters long. In 2016, Gregory S. Paul estimated its length at 1 m (3.3 ft) and its body mass at 4 kg (8.8 lb); he also suggested that the holotype possibly belongs to a juvenile.[4] The ilium is elongated and low with the typical tyrannosauroid vertical ridge on the outer blade surface above the hip joint.[2] The teeth of the praemaxilla have a D-shaped cross-section. The maxillary and dentary teeth are elongated, only recurving near the top, with perpendicular denticles on both edges. Their bases are circular in cross-section; the top of the tooth crown is more flattened.[3]
Classification
Aviatyrannis was in 2003 by Rauhut placed in the Tyrannosauroidea, in a basal position.[2] If this placement is correct, Aviatyrannis is one of the oldest tyrannosauroids ever found, the oldest being Proceratosaurus (or, possibly, Iliosuchus).[2] However, a 2023 paper by Hattori et al. noted that the Aviatyrannis ilium is strikingly similar to that of the newly described deinocheirid Tyrannomimus. The authors argue that, though more detailed study is needed, Aviatyrannis could be the earliest known ornithomimosaur. The results of their phylogenetic analyses are displayed in the cladogram below:[5]
| Ornithomimosauria |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
See also
References
- ^ Rauhut, O.W.M., 2000, "The dinosaur fauna from the Guimarota mine", pp 75-82 In: Martin and Krebs (eds.). Guimarota - A Jurassic Ecosystem Verlag Dr. Friedrich Pfeil, München
- ^ a b c d e f g h i Oliver W. M. Rauhut. (2003). "A tyrannosauroid dinosaur from the Upper Jurassic of Portugal". Palaeontology. 46 (5): 903–910. doi:10.1111/1475-4983.00325.
- ^ a b Zinke, J., 1998, "Small theropod teeth from the Upper Jurassic coal mine of Guimarota (Portugal)", Paläontologische Zeitschrift 72(1/2): 179-189
- ^ Paul, Gregory S. (2016). The Princeton Field Guide to Dinosaurs. Princeton University Press. p. 106. ISBN 978-1-78684-190-2. OCLC 985402380.
- ^ Hattori, Soki; Shibata, Masateru; Kawabe, Soichiro; Imai, Takuya; Nishi, Hiroshi; Azuma, Yoichi (2023-09-07). "New theropod dinosaur from the Lower Cretaceous of Japan provides critical implications for the early evolution of ornithomimosaurs". Scientific Reports. 13 (1): 13842. doi:10.1038/s41598-023-40804-3. ISSN 2045-2322. PMC 10484975.















