The pous (pl. podes; Greek: πούς, poús) or Greek foot (pl. feet) was a Greek unit of length. It had various subdivisions whose lengths varied by place and over time. 100 podes made up one plethron, 600 podes made up a stade (the Greek furlong) and 5000 made up a milion (the Greek mile). The Greek pous also has long, median and short forms.
The pous spread throughout much of Europe and the Middle East during the Hellenic period preceding and following the conquests of Alexander the Great and remained in use as a Byzantine unit until the Fall of Constantinople in 1453.
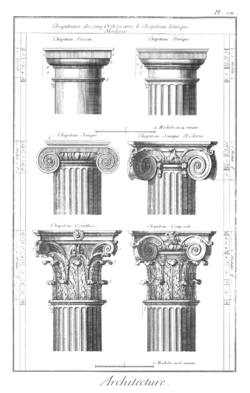
Comparative analysis
A pous is divided into digits or fingers (daktyloi) which are multiplied as shown. Generally the sexagesimal or decimal multiples have Mesopotamian origins while the septenary multiples have Egyptian origins.
Greek measures of short median and long podes can be thought of as based on body measures. The lengths may be compared to the Imperial/U.S. foot of 304.8 mm. Stecchini and others propose the Greek podes are different sizes because they are divided into different numbers of different sized daktylos to facilitate different calculations. The most obvious place to observe the relative difference is in the Greek orders of architecture whose canon of proportions is based on column diameters.
| Unit | no. of daktyloi | each daktylos (mm) | total (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 Doric order pous (foot) | 18 | 18 | 324 mm |
| 1 Luwian pous (foot) | 17 | 19 | 323 mm |
| 1 Attic pous (foot) | 16 | 19.275 | 308.4 mm |
| 1 Minoan pous (foot) | 16 | 19 | 304 mm |
| 1 Egyptian bd (foot) | 16 | 18.75 | 300 mm |
| 1 Ionian Order pous (foot) | 16 | 18.5 | 296 mm |
| 1 Roman pes (foot) | 16 | 18.5 | 296 mm |
| 1 Athenian pous (foot) | 15 | 21 | 315 mm |
| 1 Phoenician (Pele) pous (foot) | 15 | 20 | 300 mm |
References
Mathematical and metrological references
- H Arthur Klein (1976). The World of Measurements. Simon and Schuster.
- R. A. Cordingley (1951). Norman's Parallel of the Orders of Architecture. Alex Trianti Ltd.
- Francis H. Moffitt (1987). Surveying. Harper & Row. ISBN 0-06-044554-8.
- Gillings (1972). Mathematics in the time of the Pharaohs. MIT Press. ISBN 0-262-07045-6.
- Lucas N. H. Bunt; Phillip S.Jones; Jack D. Bedient (1976). The Historical Roots of Elementary Mathematics. Dover. ISBN 0-486-25563-8.
- Somers Clarke & R. Englebach (1990). Ancient Egyptian Construction and Architecture. Dover. ISBN 0-486-26485-8.
- Gardiner (1990). Egyptian Grammar. Griffith Institute. ISBN 0-900416-35-1.
Linguistic references
- Anne H. Groton (1995). From Alpha to Omega. Focus Information group. ISBN 0-941051-38-2.
- J. P. Mallory (1989). In Search of the Indo Europeans. Thames and Hudson. ISBN 0-500-27616-1.
Classical references
- Vitruvius (1960). The Ten Books on Architecture. Dover.
- Claudias Ptolemy (1991). The Geography. Dover. ISBN 0-486-26896-9.
- Herodotus (1952). The History. William Brown.
Archaeological historical references
- Michael Grant (1987). The Rise of the Greeks. Charles Scribner's Sons. ISBN 9780684185361.
- Lionel Casson (1959). The ancient mariners: seafarers and sea fighters of the Mediterranean in ancient times. Macmillan. OCLC 392365.
- James B. Pritchard (1968). The Ancient Near East. OUP.
- Nelson Glueck (1959). Rivers in the Desert. HUC.
Medieval references
- Jean Gimpel (1976). The Medieval Machine. Holt Rheinhart & Winston. ISBN 0-03-014636-4.
- H Johnathan Riley Smith (1990). The Atlas of the Crusades. Swanston. ISBN 0-7230-0361-0.
- Elizabeth Hallam (1986). The Plantagenet Chronicles. Weidenfeld & Nicolson. ISBN 1-55584-018-3.
- H.W. Koch (1978). Medieval Warfare. Prentice Hall. ISBN 0-13-573600-5.
