| Amphilinidae | |
|---|---|
| |
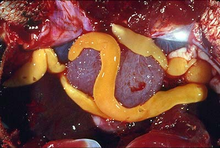
| Australamphilina elongata | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Platyhelminthes |
| Class: | Cestoda |
| Subclass: | Cestodaria |
| Order: | Amphilinidea Poche, 1922 [1] |
| Family: | Amphilinidae Claus, 1879 |
| Genera | |
|
See text | |
| Synonyms | |
| |
Amphilinidae is a family of parasitic flatworms of the phylum Platyhelminthes. It is the only family in the monotypic order Amphilinidea. Amphilinids are Cestodes, yet differ from true tapeworms (Eucestoda) as their bodies are unsegmented and not divided into proglottids.[2] "Amphilinids are large worms which have a flattened leaf-like body. Only 8 amphilinid species are known."[3] "The adults are hermaphroditic. A muscular proboscis is located at the anterior end, and is sometimes very weakly developed or absent."[4] They live in the body cavities of freshwater turtles and teleost fish as adults, and in the bodies of various crustaceans as juveniles.[5] Apart from a little studied parasitism of sturgeon, these flatworms have very little economic importance. Biologically, they have gained attention for their potential to shed light on the phylogeny of tapeworms.[3]
YouTube Encyclopedic
-
1/3Views:3 9861 1874 409
-
Tapeworm facts: found in a body near you | Animal Fact Files
-
Zoology PPR 1 Lower Non-Chordata (Protozoa to Helminths) BSC 1 previous year objective qn ppr Video
-
Taenia solium-1||Most important MCQ||Phyum-Platyhelminthes||B Sc 1st Year||Zoology||
Transcription
Subordinate taxa
- Genus Amphilina Wagener, 1858
- Amphilina foliacea (Rudolphi, 1819) Wagener, 1858
- Amphilina japonica Goto & Ishii, 1936
- Genus Australamphilina Johnston, 1931
- Australamphilina elongata Johnston, 1931
- Genus Gephyrolina Poche, 1926
- Gephyrolina paragonopora (Woodland, 1923)
- Genus Gigantolina Poche, 1922
- Gigantolina magna (Southwell, 1915) Poche, 1922
- Gigantolina raebareliensis Srivastav, Mathur & Rani, 1994
- Genus Nesolecithus Poche, 1922
- Nesolecithus africanus Dönges & Harder, 1966
- Nesolecithus janickii Poche, 1922
- Genus <i>Schizochoerus</i> Poche, 1922
- Schizochoerus liguloides (Diesing, 1850)
References
- ^ Rod Bray (2010). "Amphilinidea". WoRMS. World Register of Marine Species. Retrieved December 5, 2011.
- ^ Klaus Rohde (June 2, 2011). "The Amphilinidea, a small group of aberrant tapeworms". Knol. Archived from the original on 2011-08-13. Retrieved December 5, 2011.
- ^ a b Klaus Rohde. "Amphilinidea. Amphilinidae. Version 05". Tree of Life Web Project. Retrieved December 1, 2011.
- ^ Klaus Rohde. "Amphilinidea". AccessScience. McGraw-Hill. doi:10.1036/1097-8542.030100. Retrieved December 6, 2011.
- ^ Klaus Rohde. "Amphilinidea life cycles". Tree of Life Web Project. Retrieved December 6, 2011.
