

In organic chemistry, hydrocarbons (compounds composed solely of carbon and hydrogen) are divided into two classes: aromatic compounds and aliphatic compounds (/ˌælɪˈfætɪk/; G. aleiphar, fat, oil). Aliphatic compounds can be saturated (in which all the C-C bonds are single requiring the structure to be completed, or 'saturated', by hydrogen) like hexane, or unsaturated, like hexene and hexyne. Open-chain compounds, whether straight or branched, and which contain no rings of any type, are always aliphatic. Cyclic compounds can be aliphatic if they are not aromatic.[1]
YouTube Encyclopedic
-
1/1Views:1 259
-
Tele Liban - E-learning - Grade 9 - Chemistry - Classification of Aliphatic Hydrocarbons
Transcription
Structure
Aliphatic compounds can be saturated, joined by single bonds (alkanes), or unsaturated, with double bonds (alkenes) or triple bonds (alkynes). If other elements (heteroatoms) are bound to the carbon chain, the most common being oxygen, nitrogen, sulfur, and chlorine, it is no longer a hydrocarbon, and therefore no longer an aliphatic compound. However, such compounds may still be referred to as aliphatic if the hydrocarbon portion of the molecule is aliphatic, e.g. aliphatic amines, to differentiate them from aromatic amines.
The least complex aliphatic compound is methane (CH4).
Properties
Most aliphatic compounds are flammable, allowing the use of hydrocarbons as fuel, such as methane in natural gas for stoves or heating; butane in torches and lighters; various aliphatic (as well as aromatic) hydrocarbons in liquid transportation fuels like petrol/gasoline, diesel, and jet fuel; and other uses such as ethyne (acetylene) in welding.
Examples of aliphatic compounds
The most important aliphatic compounds are:
- n-, iso- and cyclo-alkanes (saturated hydrocarbons)
- n-, iso- and cyclo-alkenes and -alkynes (unsaturated hydrocarbons).
Important examples of low-molecular aliphatic compounds can be found in the list below (sorted by the number of carbon-atoms):
| Formula | Name | Structural formula | Chemical classification |
|---|---|---|---|
| CH4 | Methane | 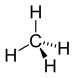 |
Alkane |
| C2H2 | Acetylene | Alkyne | |
| C2H4 | Ethylene |  |
Alkene |
| C2H6 | Ethane |  |
Alkane |
| C3H4 | Propyne | Alkyne | |
| C3H6 | Propene | 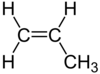 |
Alkene |
| C3H8 | Propane |  |
Alkane |
| C4H6 | 1,2-Butadiene |  |
Diene |
| C4H6 | 1-Butyne |  |
Alkyne |
| C4H8 | 1-Butene | Alkene | |
| C4H10 | Butane | 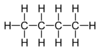 |
Alkane |
| C6H10 | Cyclohexene | Cycloalkene | |
| C5H12 | n-pentane | Alkane | |
| C7H14 | Cycloheptane | Cycloalkane | |
| C7H14 | Methylcyclohexane | 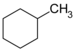 |
Cyclohexane |
| C8H8 | Cubane |  |
Prismane, Platonic hydrocarbon |
| C9H20 | Nonane | Alkane | |
| C10H12 | Dicyclopentadiene |  |
Diene, Cycloalkene |
| C10H16 | Phellandrene |   |
Terpene, Diene, Cycloalkene |
| C10H16 | α-Terpinene | Terpene, Diene, Cycloalkene | |
| C10H16 | Limonene |  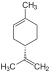 |
Terpene, Diene, Cycloalkene |
| C11H24 | Undecane | Alkane | |
| C30H50 | Squalene | Terpene, Polyene | |
| C2nH4n | Polyethylene | Alkane |
References
- ^ IUPAC, Compendium of Chemical Terminology, 2nd ed. (the "Gold Book") (1997). Online corrected version: (1995) "aliphatic compounds". doi:10.1351/goldbook.A00217
