Agate VE 110 | |
| Function | Sounding rocket |
|---|---|
| Manufacturer | SEREB |
| Country of origin | France |
| Size | |
| Height | 8.50 metres (27.9 ft) |
| Diameter | 0.80 metres (2.6 ft) |
| Mass | 3,200 kilograms (7,100 lb) |
| Stages | 1 |
| Associated rockets | |
| Derivative work | Rubis, Diamant |
| Launch history | |
| Status | Retired |
| Launch sites | CIEES/CERES Ile du Levant |
| Total launches | 12 |
| Success(es) | 11 |
| Failure(s) | 1 |
| First flight | June 3, 1961 |
| Last flight | April 20, 1964 |
| First stage | |
| Powered by | NA801 Mammouth |
| Maximum thrust | 186 kilonewtons (42,000 lbf) |
| Propellant | Solid |
VE 110 Agate is the designation of an unguided French test rocket developed in the late 1950s and early 1960s.[1][2][3]
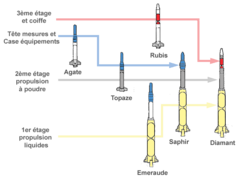
It was part of the Pierres précieuses (fr.: gemstones) program, that included five prototypes Agathe, Topaze, Emeraude, Rubis and Saphir,[3] leading up to the Diamant orbital rocket.
The Agate has a length of 8.50 metres, a diameter of 0.80 metres, a start mass of 3.2 tonnes, a takeoff thrust of 186 kN and a ceiling of 20 km. It used a NA801 Mammouth solid propellant rocket engine (same as the Rubis VE-210).[2]
The initial version was designated VE (Véhicule Expérimental) 110,[1][3] while the VE 110RR version was used to develop recovery procedures at sea.[2][3] The name indicates that it is a "Véhicule Expérimental" (Experimental Vehicle) with 1 stage, using solid propulsion (code 1), and not guided (code 0).
-
-
Agate and Rubis rockets
YouTube Encyclopedic
-
1/3Views:42232 654301
-
Rocket's Rock Tumbling 1: Mexican Lace & Botswana Agate
-
Quartz, chalcedony, chert, jasper and agate: the differences between them!
-
Rocket's Rock Tumbling 2: Mexican Lace Agate, Botswana Agate, and Rose Quartz
Transcription
Launches
The Agate was launched from the CIEES test site in Hammaguir, French Algeria, and the Île du Levant test site,[2] in order to test instrument capsules and recovery systems.[3]
| Date | Launch Site | Launch Complex | Mission Description | Apogee (km) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1961 June 3 | Hammaguira | Hammaguira Bacchus | Test mission | 20 |
| 1961 June 7 | Hammaguira | Hammaguira Bacchus | Test mission | 20 |
| 1961 Nov 13 | Hammaguira | Hammaguira Bacchus | Test mission | 20 |
| 1961 Nov 17 | Hammaguira | Hammaguira Bacchus | Test mission | 20 |
| 1962 Mar 19 | Hammaguira | Hammaguira Bacchus | Test mission | 20 |
| 1962 Mar 23 | Hammaguira | Hammaguira Bacchus | Test mission | 20 |
| 1963 May 18 | Hammaguira | Hammaguira Brigitte | Test mission | 20 |
| 1963 May 21 | Hammaguira | Hammaguira Brigitte | Test mission | 20 |
| 1963 Nov 19 | Île du Levant | CERES | Failure | 0 |
| 1963 Nov 28 | Ile du Levant | CERES | Test mission | 20 |
| 1964 Feb 28 | Ile du Levant | CERES | Test mission | 20 |
| 1964 Apr 20 | Ile du Levant | CERES | Test mission | 20 |
See also
References