
Abraham and Isaac is a sacred ballad for baritone and orchestra composed in 1962–63 by Igor Stravinsky.
YouTube Encyclopedic
-
1/3Views:11 837 2121 7551 900
-
Samuel Barber - Adagio for Strings
-
Benjamin Britten - A Time There Was by Tony Palmer
-
MORDECHAI SETER : Sabbath cantate May 1968 live conducted by Gary Bertini
Transcription
History
When the Israel Festival Committee asked Stravinsky for a new work, he decided to set the story of Abraham and Isaac to a text in Hebrew, a language with which he was not familiar. The philosopher Sir Isaiah Berlin, who was a friend of the composer, helped Stravinsky to understand the sounds and structure of the text. Work was begun in 1962 and the score, which is dedicated to the people of the State of Israel, was completed on 3 March 1963. The work was premiered on 23 August 1964 in Binyanei Ha'Ooma, Jerusalem, by Ephraim Biran, baritone, and the Israel Festival Orchestra, conducted by Robert Craft.[1]
Scoring
Abraham and Isaac is set for baritone solo and a chamber orchestra consisting of two flutes, alto flute, oboe, cor anglais, clarinet, bass clarinet, two bassoons, horn, two trumpets, tenor trombone, bass trombone, tuba, and string quintet.
Analysis
Although Stravinsky described the work as falling into five parts, played continuously but marked by changes of tempo, double bars divide the score into seven sections:[2]
- Bars 1–72,
 = 132
= 132 - Bars 73–90,
 = 132 (Stesso tempo)
= 132 (Stesso tempo) - Bars 91–104,
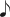 = 120
= 120 - Bars 105–162,
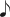 = 92–96 (Meno mosso)
= 92–96 (Meno mosso) - Bars 163–181,
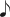 = 76 (Meno mosso)
= 76 (Meno mosso) - Bars 182–239,
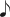 = 72 (Meno mosso)
= 72 (Meno mosso) - Bars 240–254,
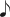 = 60 (Andante)
= 60 (Andante)
The work is based on a twelve-tone row, elaborated into hexachordal rotational arrays.[3] Stravinsky often employs the columns from these arrays, which he called "verticals", to form canonic chordal successions.[4] The basic form of the row is G A♭ B♭ C D♭ A B E♭ D E G♭ F and is therefore interval class palindromic, with interval classes 1–2–2–1–4–2–4–1–2–2–1.[5]
References
Citations
- ^ White 1979, p. 528.
- ^ White 1979, pp. 530–531.
- ^ Straus 2001, pp. 106–109.
- ^ Straus 2001, pp. 152–153, 158–159.
- ^ Smyth 1999, pp. 134–135, 142.
Sources
- Smyth, David. 1999. "Stravinsky's Second Crisis: Reading the Early Serial Sketches". Perspectives of New Music 37, no. 2 (Summer): 117–146.
- Straus, Joseph N. 2001. Stravinsky's Late Music. Cambridge Studies in Music Theory and Analysis. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-521-60288-2.
- White, Eric Walter. 1979. Stravinsky: The Composer and His Works, second edition. Berkeley and Los Angeles: The University of California Press. ISBN 0-520-03985-8.
Further reading
- Payne, Anthony (Summer 1965). "Stravinsky's 'Abraham and Isaac' and 'Elegy for J. F. K.'". Tempo. Cambridge University Press (73): 12–15. JSTOR 942857.
