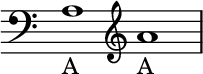
A or La is the sixth note and the tenth semitone of the fixed-do solfège.
Its enharmonic equivalents are B♭♭ (B double flat) which is a diatonic semitone above A♭ and G![]() (G double sharp) which is a diatonic semitone below A♯.
(G double sharp) which is a diatonic semitone below A♯.
"A" is generally used as a standard for tuning. When the orchestra tunes, the oboe plays an "A" and the rest of the instruments tune to match that pitch. Every string instrument in the orchestra has an A string, from which each player can tune the rest of their instrument.
"A" is also used in combination with a number (e.g. A-440) to label the pitch standard. The number designates the frequency in hertz. A lower number indicates a lower pitch.
The International Standards Organization (ISO) has standardized the pitch at A-440.[1] However, tuning has varied over time, geographical region, or instrument maker. In 17th-century Europe, tunings ranged from about A-374 to A-403, approximately two to three semitones below A-440. Historical examples exist of instruments, tuning forks, or standards ranging from A-309 to A-455.3,[2] a difference of almost six semitones. Although the official standard today is A-440, some orchestral groups and chamber groups prefer to tune a little higher, at A-442 or even A-444. Baroque pitch is usually cited as A-415, which is a semitone lower than modern pitch.
A0 is the lowest note on the standard piano. The octaves follow A1, A2, etc. A7 is a few pitches lower than C8, the highest note on the standard piano. The note "A" is not considered to be a certain milestone or mark to hit with voice as, for example, Tenor C is, but it can be extremely demanding in certain octaves.
YouTube Encyclopedic
-
1/3Views:495 0631 299 0181 096 680
-
Music Notes | Notes | Green Bean's Music
-
Musical Notes! Learning about music for Kids
-
Musical Notation - Learning Music for Kids - The quarter note, the half note and the whole note
Transcription
Designation by octave
| Scientific designation |
Helmholtz designation |
Octave name |
Frequency (Hz) |
Sound sample |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A−1 | A͵͵͵ or ͵͵͵A or AAAA | Subsubcontra | 13.75 | |
| A0 | A͵͵ or ͵͵A or AAA | Subcontra | 27.5 | |
| A1 | A͵ or ͵A or AA | Contra | 55 | |
| A2 | A | Great | 110 | |
| A3 | a | Small | 220 | |
| A4 | a′ | One-lined | 440 | |
| A5 | a′′ | Two-lined | 880 | |
| A6 | a′′′ | Three-lined | 1760 | |
| A7 | a′′′′ | Four-lined | 3520 | |
| A8 | a′′′′′ | Five-lined | 7040 | |
| A9 | a′′′′′′ | Six-lined | 14080 | |
| A10 | a′′′′′′′ | Seven-lined | 28160 |
Scales
Common scales beginning on A
- A major: A B C♯ D E F♯ G♯ A
- A natural minor: A B C D E F G A
- A harmonic minor: A B C D E F G♯ A
- A melodic minor ascending: A B C D E F♯ G♯ A
- A melodic minor descending: A G F E D C B A
Diatonic scales
- A Ionian: A B C♯ D E F♯ G♯ A
- A Dorian: A B C D E F♯ G A
- A Phrygian: A B♭ C D E F G A
- A Lydian: A B C♯ D♯ E F♯ G♯ A
- A Mixolydian: A B C♯ D E F♯ G A
- A Aeolian: A B C D E F G A
- A Locrian: A B♭ C D E♭ F G A
Jazz melodic minor
- A Ascending melodic minor: A B C D E F♯ G♯ A
- A Dorian ♭2: A B♭ C D E F♯ G A
- A Lydian augmented: A B C♯ D♯ E♯ F♯ G♯ A
- A Lydian dominant: A B C♯ D♯ E F♯ G A
- A Mixolydian ♭6: A B C♯ D E F G A
- A Locrian ♮2: A B C D E♭ F G A
- A Altered: A B♭ C D♭ E♭ F G A
See also
References
- ^ "ISO 16:1975 Acoustics - Standard Tuning Frequency". International Standards Organization. Retrieved 10 December 2019.
- ^ Suits, B. H. (1998). "Physics of Music Notes - Scales: Just vs Equal Temperament". MTU.edu. Michigan Technological University. Retrieved 5 February 2024.
External links
- Standard Pitch or Concert Pitch for Pianos by Barrie Heaton
- Virginia Tech Music Dictionary: A Archived 2006-06-18 at the Wayback Machine
