| |||
7 governors, 8 mayors, and 76 regents | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Registered | ± 41,000,000 | ||
|
| |||
| |||

Local elections were held in Indonesia on 15 February 2017, with a single run-off for Jakarta on 19 April 2017. The series of elections was the second time local elections were held simultaneously across the country after the 2015 local elections. In total, the election contested 7 gubernatorial, 18 mayoral and 76 regent seats with 41 million eligible voters and 337 candidate pairs.[1]
Like other local elections in Indonesia (except for Jakarta), the elections followed a simple majority, first-past-the-post system where the candidates with the most votes automatically wins the seat even if they have less than 50% of the votes.[2]
YouTube Encyclopedic
-
1/5Views:2 0218764259 41786 115 492
-
Results of the Indonesian Elections: New Directions or More of the Same?
-
Democracy for Sale: Elections, Clientelism, and the State in Indonesia
-
The 2017 Austrian Elections and their Consequences
-
UK Election Day English - June 8th 2017 - Live English Lesson Stream
-
Yes Yes Playground Song + @Cocomelon - Nursery Rhymes | Videos For Kids | Moonbug Kids
Transcription
Background
Following the fall of Suharto and the Indonesian transition to democracy, local elections began taking place allowing citizens to directly vote for leaders of local subdivisions in June 2005, which had previously been elected through a closed vote by the local legislative councils (Indonesian: Dewan Perwakilan Rakyat Daerah/DPRD).[3] These elections were held separately for both provincial and municipal (cities and regencies) levels, resulting in on average an election every 3 days across the country according to the director-general of regional autonomy Djohermansyah Djohan. Between June 2005 and 2013, around 1,000 such elections were held prompting the discussion of a single simultaneous election to save costs.[4]
Simultaneous local elections (Pilkada Serentak) were first held in Indonesia on 2015.[5] Future plans for the elections included ones in 2017, 2018 and 2020, with appointed central government officials taking office instead for 2022 and 2023. It was planned that by 2024 the local executive elections could be held simultaneously with the presidential and legislative elections.[6]
Schedule
Registration for candidates were separated into tickets supported by political parties and independent candidates who were required to prove popular support by submitting copies of ID cards, the quantity of which ranged from 6.5 to 10 percent of the area's number of eligible voters depending on the local population in accordance to Law No. 8 of 2015.[7][8] The latter were required to register to the General Elections Commission (Indonesian: Komisi Pemilihan Umum) between 6 and 10 August 2016. Tickets backed by a political party or a coalition of such required the parties to have the cumulative support of either 20 percent of DPRD seats or 25 percent of the popular vote in the 2014 legislative election,[9] and were to register between 19 and 21 September 2016.[10] After a verification process, official candidates were announced on 24 October 2016 and the ballot numbers were given out on the following day. The campaigning period commenced on 28 October and continued until 11 February the following year. A three-day election silence followed, and the votes were cast on 15 February.[10]
After the wave of elections, the votes were recapitulated and counted. Official announcement of the results were done between 8 and 10 March 2017, and the winners given official status by the Constitutional Court subject to disputes.[10] For the case of Jakarta, a majority vote was required to win the election, which was not obtained from the 15 February vote and required a run-off on 19 April.[11] The results of Jakarta's run-off was announced on 30 April.[12]
According to data by the Ministry of Home Affairs, the elections used up Rp 7 trillion (US$520 million). Minister Tjahjo Kumolo stated that the elections were less efficient and required more funding than the previous system of individual elections.[13]
Elections
Gubernatorial
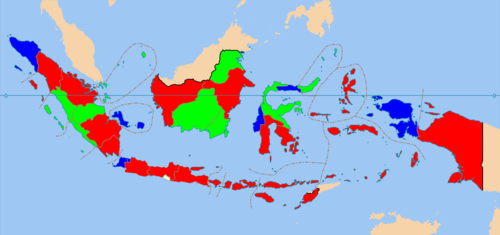
Note: name in italics indicate incumbents who ran for re-election
Mayoral
Regent
References
- ^ Chan, Francis (13 February 2017). "Key things to know about Indonesia's regional elections on Wednesday". The Straits Times. Retrieved 22 April 2018.
- ^ "Pilkada Serentak dengan Aturan Berbeda, Hanya Jakarta 50% Plus Satu". Media Indonesia (in Indonesian). 24 June 2016. Retrieved 20 January 2018.
- ^ Choi, Nankyung (August 2007). "Local elections and democracy in Indonesia: The Riau Archipelago". Journal of Contemporary Asia. 37 (3): 326–345. doi:10.1080/00472330701408650.
Under the New Order regime, local government heads were in effect appointed by the central government, despite going through a formal electoral process in the local assemblies (Dewan Perwakilan Rakyat Daerah, DPRD).
- ^ "Pilkada serentak, solusi efisiensi biaya - ANTARA News". ANTARA News (in Indonesian). 24 January 2015. Retrieved 22 April 2018.
- ^ Ferri, Oscar (17 April 2015). "KPU Resmikan Pelaksanaan Pilkada Serentak 2015". liputan6.com (in Indonesian). Retrieved 5 January 2018.
- ^ Tashandra, Nabilla (6 June 2016). "Penyelenggaraan Pilkada dan Pemilu secara Serentak pada 2024 Dinilai Belum Jelas". KOMPAS (in Indonesian). Retrieved 22 April 2018.
- ^ Afriana, Rina (29 September 2015). "Putusan MK Ringankan Calon Independen Berlaga di Pilkada 2017". Detik (in Indonesian). Retrieved 22 April 2018.
- ^ "Undang Undang No. 8 Tahun 2015" (PDF). dpr.go.id (in Indonesian). Archived from the original (PDF) on 28 March 2018. Retrieved 22 April 2018.
- ^ "Tiga Syarat Pencalonan yang Berasal Dari Parpol" (in Indonesian). Komisi Pemilihan Umum. Retrieved 22 April 2018.
- ^ a b c "Tahapan pada Pilkada 2017" (in Indonesian). Komisi Pemilihan Umum. Retrieved 22 April 2018.
- ^ "Ahok makes it to run-off in Jakarta governor race". The Guardian. 5 March 2017. Retrieved 22 April 2018.
- ^ "Anies Baswedan-Sandiaga Uno Announced as Jakarta Election Winner". Tempo. 30 April 2017. Retrieved 22 April 2018.
- ^ Sidik, Syahrizal (22 January 2018). "Mendagri: Biaya Pilkada Serentak Lebih Boros Dibanding Penyelenggaraan Pilkada Satuan". Tribun News (in Indonesian). Retrieved 22 April 2018.
- ^ a b c "HASIL PERHITUNGAN SUARA PILKADA 2017" (in Indonesian). Komisi Pemilihan Umum. Retrieved 22 April 2018.
- ^ a b c "Ini 101 Daerah yang Gelar Pilkada Serentak 2017". Liputan6 (in Indonesian). 16 February 2016. Retrieved 22 April 2018.
